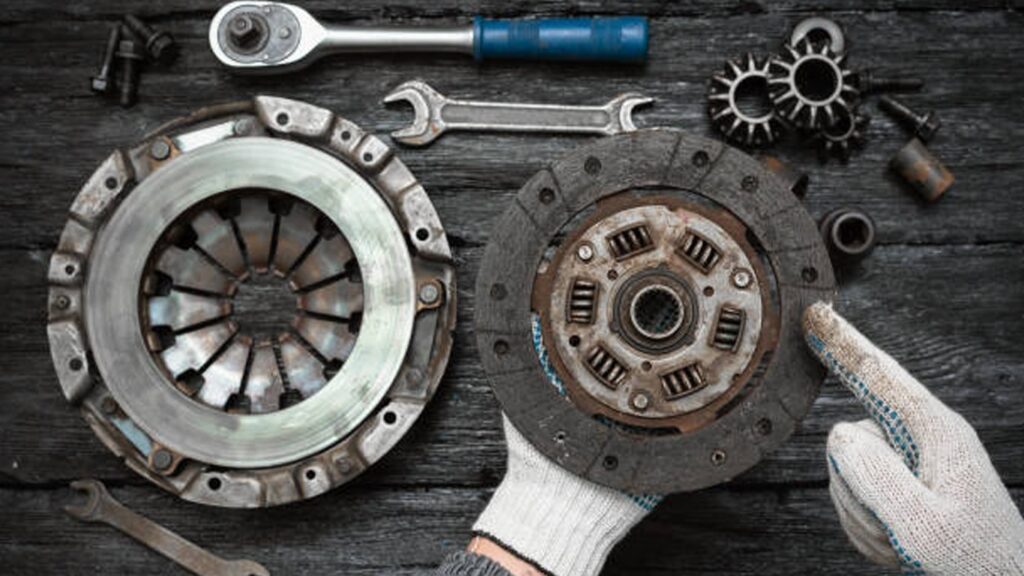
A centrifugal clutch is a type of clutch typically used with combustion engines and is used on driven rotary equipment. It can be most commonly found in small machinery such as lawnmowers, mopeds, chainsaws, and other technology with idling speed capabilities. FCC has been manufacturing state-of-the-art clutch technology since 1939. Explore our advanced clutch solutions today.
How does a centrifugal clutch work?
The primary duty of a clutch is to engage and disengage power between the engine and transmission, giving machinery access to smooth power delivery and gear changes. The centrifugal clutch employs centrifugal force—a type of force that acts outward on a body moving around a center—and gives machinery the ability to allow for a “soft start” with no load engagement. The user can then control the speed at which the mechanical driven shaft engages. The operator can run the engine at an idling speed without actually driving the equipment, letting the engine reach its optimal torque before it experiences load.
Our in-house innovation team, automated and manual quality checks, and careful consideration for the safety of you and your customers has allowed us to leave our mark on the clutch manufacturing industry for over 85 years.
Key components that enable clutch duties
There are several components that help a clutch function optimally, including:
- Flywheights: The flywheights are connected to the engine crankshaft, which provides a smooth surface for the clutch disc to engage with. This is where the centrifugal force is transmitted.
- Clutch Disc: A friction-lined disc that transfers power from the engine to the transmission when engaged. This is a common component on clutches, and helps channel the generated force into power for the engine.
- Pressure Plate: The pressure plate applies force to keep the clutch disc pressed against the flyweights during normal operation.
- Release Bearing: On a typical clutch, this component allows the pressure plate to disengage when the clutch pedal is pressed.
- Pilot Bearing: The pilot bearing supports the transmission input shaft, which helps the engine operate smoothly.
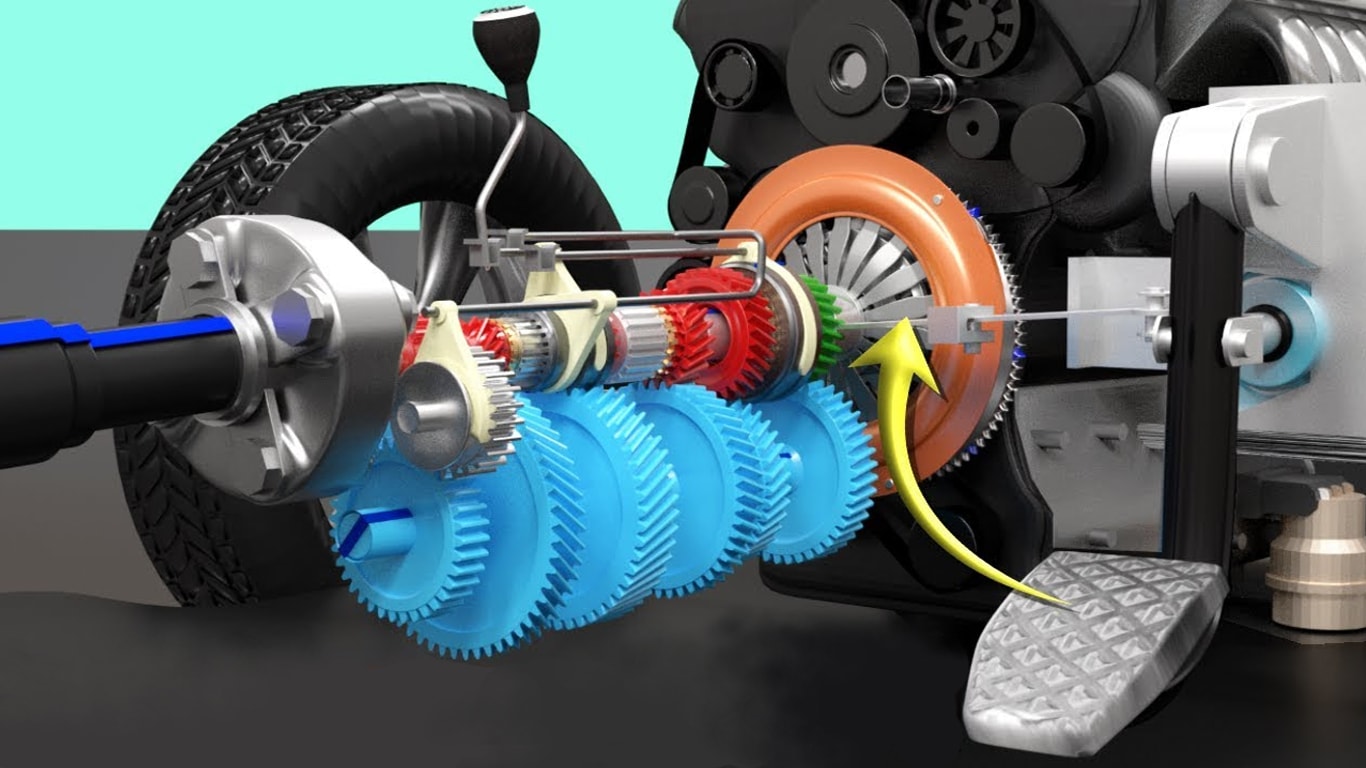
The friction material, such as that employed by the clutch disc, are what help determine the speed at which the centrifugal clutch engages. The friction is what generates the torque to power the engine.
Applications for a centrifugal clutch
A centrifugal clutch can prove optimal in a variety of applications. Most commonly, it can be found in the following:
- Lawnmowers: Typically, centrifugal clutches in lawnmowers are most often found in race mowers, given that the centrifugal clutch allows the user to control speed.
- Mopeds: A centrifugal clutch’s ability to give a machine the ability to operate idly and change speed quickly makes it ideal for mopeds.
- Go-karts: Similar to a moped, centrifugal clutches are often used in go-karts because the engine is able to run while the go-kart is stationary. This allows for a quick and easy transfer of power when the user is ready to move again.
- Chainsaws: A chainsaw can be idle in a user’s hands without actively sawing something, making a centrifugal clutch the most optimal clutch for this application.
- Vibratory plate compactors and rollers: Centrifugal clutches can be particularly useful in vibratory plate compactors and rollers, as they will not engage until the vibrations reach a certain speed. This means the engine can start and stop without engaging the plate.
- Rammers: With a centrifugal clutch, a rammer’s power can be easily engaged and disengaged, allowing for smooth power transfer and reducing the risk of damage to the rammer.
- Compressor/vacuum/fan drives: When centrifugal force is applied to these devices, it allows for the “soft start” the centrifugal clutch is known for. It also reduces the chance of shock as they only engage when the engine reaches a certain speed.
- Trowel and concrete finishers: A centrifugal clutch can enhance the safety measures in these applications, as the drive system will immediately disengage when the user releases the handle and force is no longer transmitting through the application.
- Compact road/street cleaners: Centrifugal clutches are ideal in applications such as compact road and street cleaners since they allow for a soft start or a soft stop.
- Transport refrigeration units: In this application, centrifugal clutches act like a coupling unit. Torque is transferred from the engine to the compressor, which helps prevent engine stalling.
Maintaining your clutch for optimal performance
Proper care of your clutch is vital for ensuring your application and the clutch itself has a long lifespan. In the event your clutch breaks, or you need specialized components for your application, our experts are constantly innovating new ways to revolutionize clutch performance.
To maintain your clutch, avoiding overloading is key. Users should also use caution when shifting, and aim for a smooth transition if possible. This will help avoid excess stress on the clutch disc and pressure plate, which are key for facilitating torque throughout the clutch. The additional strain will cause the components to wear out faster.
If your clutch is ready to be replaced, you can contact our experts and find the right parts for your application.
Summary
When trying to maximize your application’s performance, understanding the key functions and uses of the clutch is critical. Knowing how a centrifugal clutch works—and where best it can work—will help your applications perform not just as intended, but for more time and more successfully.
Since 1939, FCC has been on the forefront of clutch development. From tried and true manufacturing to new and innovative technologies, FCC will guide you through the correct clutch for your application. Contact our experts for customized clutch solutions.
FAQs
How does a centrifugal clutch work?
A centrifugal clutch is a type of clutch typically used with combustion engines and is used on driven rotary equipment. It can be most commonly found in small machinery such as lawnmowers, mopeds, chainsaws, and other technology with idling speed capabilities.
How does a centrifugal clutch differ from a traditional clutch?
The centrifugal clutch employs centrifugal force—a type of force that acts outward on a body moving around a center—and gives machinery the ability to allow for a “soft start” with no load engagement. The clutch is engaged based on the speed of the machine. A traditional clutch, however, requires manual engagement.
What are the main applications of centrifugal clutches?
A centrifugal clutch can prove optimal in a variety of applications. It is typically found in applications where clutch engagement is based on the speed of the machine, such as lawnmowers, mopeds, go-karts, chainsaws, and other devices capable of “idling” speeds.
Can centrifugal clutches be used in all types of engines?
No, centrifugal clutches are generally best in smaller, simpler applications. Centrifugal clutches can slip if the loads are too heavy, which means they are not ideal for heavy load-bearing machinery.
What are the advantages of using a centrifugal clutch in motor applications?
A centrifugal clutch allows for smooth power transition, smooth gear shifts, and the ability to soft start or soft stop as needed. The centrifugal clutch components also do not typically engage until the application reaches a certain speed, which improves the safety mechanics.
How does the engagement speed of a centrifugal clutch affect its performance?
The engagement speed of a centrifugal clutch means power transitions and gear shifts are smoother in applications that use them, and are ideal for engines that require a broad range of speed, giving them additional flexibility that other clutches may not provide.