In the ever-evolving landscape of the automotive industry, where precision and excellence are not mere aspirations but prerequisites, the role of quality engineers stands as a linchpin in the pursuit of product value.
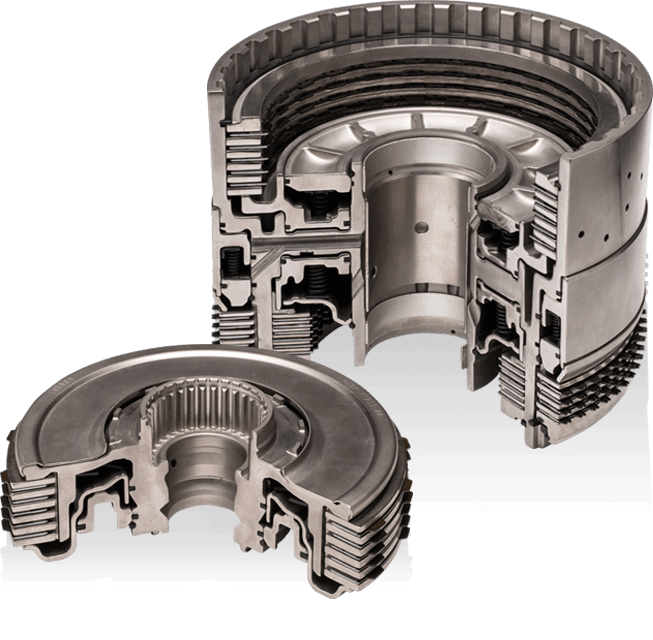
FCC, with our illustrious legacy since 1939, epitomizes the commitment to safety, quality, cost efficiency, and timely delivery. In this context, the role of quality engineering in manufacturing becomes paramount, not only to maintain but to continually enhance product value in the competitive markets they serve.
In this post, we’ll explain the role of quality engineering in manufacturing to enhance product value.
What is Quality Engineering In Manufacturing?
Quality engineering in manufacturing is a strategic and comprehensive approach to ensuring the highest standards throughout the product development lifecycle. It is more than a set of routine inspections or reactive measures; instead, it is a proactive and systematic methodology that includes every facet of the manufacturing process. At its core, quality engineering is about fostering a culture of excellence and continuous improvement.
Significance in Product Development
Quality engineering in manufacturing exceeds the conventional boundaries of quality control; it is an integral part of the product development lifecycle. The significance of quality engineering lies in its capacity to proactively address challenges and drive innovations.
As Aristotle puts it, “Quality is not an act; it is a habit.” Quality engineers cultivate this habit, ensuring that excellence is not an irregular achievement but a consistent standard.
Core Responsibilities
Quality engineers shoulder a ton of responsibilities that extend beyond routine inspections. These responsibilities are pivotal in shaping the trajectory of a product from conceptualization to consumer satisfaction.
Defining Quality Standards
Precision in defining quality standards is the fulcrum upon which the quality engineering role pivots. The careful establishment of benchmarks ensures that the end product aligns with not just industry standards but surpasses them. A proactive approach to defining quality standards positively correlates with product success rates, underscoring the strategic importance of this responsibility.
Process Optimization
Process optimization, another core responsibility, is the crucible where efficiency is forged. Quality engineers delve into the intricacies of production processes, refining them for maximum output and minimum waste.
This optimization not only ensures cost-effectiveness but also directly contributes to the enhancement of overall product value. As industry veteran James Dyson aptly notes, “Manufacturing is more than just putting parts together. It’s coming up with ideas, testing principles, and perfecting the engineering.”
Risk Mitigation Strategies
When it comes to quality engineering in manufacturing, risk is not viewed bleakly but as a challenge to be met with strategic insight. Quality engineers develop and implement risk mitigation strategies, safeguarding the product from potential pitfalls. As highlighted in a research article, an effective risk mitigation strategy is a proactive investment that pays dividends in terms of product resilience and customer satisfaction.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Collaboration across disciplines is fundamental to successful quality engineering in manufacturing, fostering an environment where diverse expertise converges for a singular purpose.
Role in Cross-Functional Teams
Quality engineers play a triple role in cross-functional teams:
- the inspector, ensuring adherence to quality benchmarks
- the collaborator, harmonizing diverse skill sets
- and the innovator propelling the team towards excellence.
Dr. Belbin’s Team Role theory supports this notion, emphasizing the importance of diverse roles within a team for optimal performance. Quality engineers, under their multidimensional role, showcase this theory, ensuring that every aspect of product development is examined and refined.
Communication Strategies
Effective communication forms the backbone of successful collaboration. Quality engineers employ transparent reporting, active listening, clear documentation, and constructive feedback as communication strategies.
These strategies not only facilitate smooth collaboration but also serve as a preemptive measure against potential issues. Effective communication ensures that the complex details of quality requirements are not lost in translation, ultimately contributing to a seamless product development process.
Integration of Technology
Quality engineering in manufacturing embraces the integration of technology, leveraging advancements to fortify its role in product development.
Automation in Quality Assurance
Automation in quality assurance expedites processes and enhances accuracy. Quality engineers harness automation to streamline routine tasks, allowing for a more nuanced focus on complex challenges. A report by McKinsey & Company emphasizes the transformative impact of automation in quality control, highlighting how it not only reduces errors but also significantly improves the speed of production. Automation, when strategically implemented, becomes a force multiplier for quality engineers, enabling them to elevate their focus on strategic initiatives.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning
The infusion of AI and machine learning augments the discerning abilities of quality engineers. These technologies empower the identification of patterns, anomalies, and potential areas for improvement, thereby elevating the overall quality assurance process.
A study underscores the role of AI in predictive quality control, stating that machine learning algorithms can predict defects with high accuracy, leading to proactive measures that prevent issues before they escalate. The symbiosis of human expertise and artificial intelligence enhances the depth and breadth of quality engineering in manufacturing, positioning it at the forefront of innovation.
Key Skills for Quality Engineers
Transitioning from roles to skills, the ability of quality engineers is anchored in a diverse skill set.
Technical Proficiency
Technical proficiency, the bedrock of quality engineering in manufacturing, demands expertise in areas such as statistical analysis, data interpretation, and a nuanced understanding of industry-specific technologies. This understanding requires a high level of technical acumen, enabling quality engineers to navigate the intricacies of manufacturing processes and identify areas for improvement.
Analytical and Problem-Solving Skills
Analytical prowess and problem-solving skills distinguish quality engineers. Their ability to examine complex issues, identify root causes, and create effective solutions contributes significantly to product value enhancement.
According to a report by the World Economic Forum, problem-solving skills are identified as one of the critical skills for the future workforce. Quality engineers, equipped with analytical thinking, not only address current challenges but also anticipate and mitigate potential issues, aligning the product development process with a proactive, problem-solving mindset.
Continuous Improvement
Quality engineers are not content with the status quo; they are relentless advocates of continuous improvement.
Feedback Loops
Feedback loops, a hallmark of quality engineering in manufacturing, facilitate a perpetual cycle of refinement. By garnering insights from various stages of product development, quality engineers ensure a dynamic response to evolving challenges.
This iterative process, as highlighted in the Total Quality Management (TQM) philosophy, fosters a culture of continuous improvement. Through feedback loops, quality engineers not only rectify deficiencies but also identify opportunities for innovation, ensuring that every iteration of a product is an improvement upon the last.
Adaptability and Flexibility
Adaptability and flexibility are not just virtues but prerequisites for quality engineers. In an ever-evolving landscape, their ability to pivot strategies and approaches ensures resilience in the face of change. Quality engineers, by embodying adaptability, position themselves as instrumental players in navigating the evolving challenges of the industry, ensuring that product development strategies align with contemporary paradigms.
Metrics for Success
In the pursuit of product value enhancement, metrics serve as navigational beacons.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are the compass guiding quality engineers. Metrics such as defect density, cycle time, and customer satisfaction indices provide tangible benchmarks for success. A study done by Aparanji et al emphasizes the role of KPIs in aligning organizational goals with performance metrics, creating a roadmap for sustained success. Quality engineers meticulously track these indicators to gauge the effectiveness of their strategies and make data-driven decisions that contribute to product value enhancement.
Measuring Customer Satisfaction
The ultimate litmus test of product value is customer satisfaction. Quality engineers employ metrics like Net Promoter Score (NPS) and customer feedback analytics to gauge and enhance the end-user experience. A survey conducted by Harvard Business Review found a direct correlation between customer satisfaction and higher share prices. Quality engineers, by measuring and improving customer satisfaction metrics, not only ensure the immediate success of a product but also contribute to brand loyalty and sustained market relevance.
Industry-Specific Applications
Learning from industry-specific applications adds an extra layer of refinement to the role of quality engineers.
Quality Standards in the Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, where precision is paramount, quality standards become non-negotiable. FCC’s legacy in serving the automotive industry underscores the critical role quality engineers play in adhering to and surpassing stringent automotive quality benchmarks. The impact of quality standards on the automotive industry, citing that stringent quality measures not only ensure safety but also contribute to brand trust and market competitiveness. Quality engineers in the automotive sector, guided by industry-specific applications, become custodians of a legacy built on precision and excellence.
Learn More About FCC’s Innovative Solutions For The Automotive Industry
Summary
In conclusion, the role of quality engineers in enhancing product value is not confined to the realm of quality control; it extends to shaping the very fabric of product development.
FCC’s enduring legacy in the automotive industry serves as a testament to the enduring importance of quality engineering in manufacturing. In a world where excellence is not a choice but an expectation, quality engineers stand as sentinels, ensuring that products not only meet but exceed the expectations of a discerning market. As industries evolve, the symbiotic relationship between quality engineers and product value becomes increasingly indispensable.
Ready To Embark On This Journey Towards Excellence?
Learn More About FCC’s Innovative Solutions For The Automotive Industry