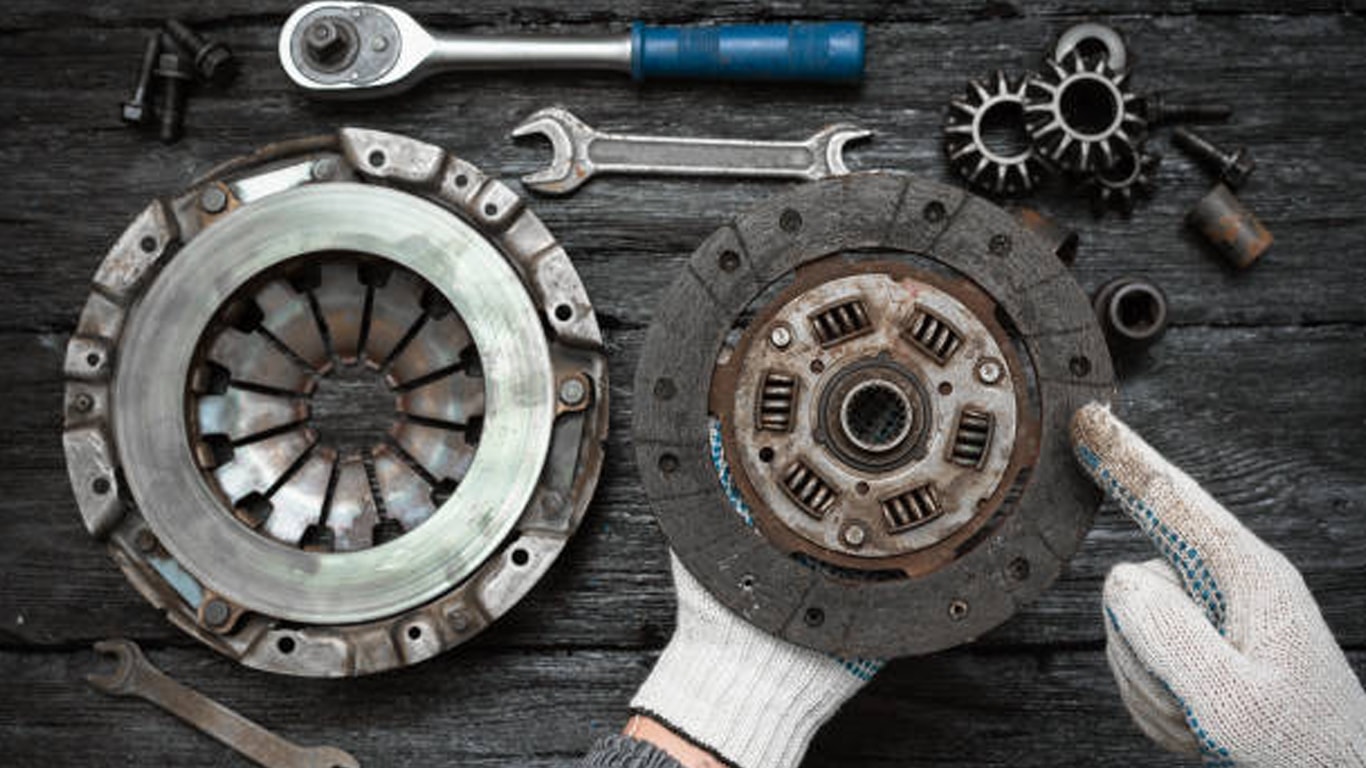
Cast aluminum is a versatile metal alloy primarily composed of aluminum with small amounts of elements like silicon, copper, magnesium, and iron. Created by melting and pouring the metal into molds, it offers excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight properties, and good machinability, making it ideal for a variety of applications.
In this blog, FCC-NA explores the practical methods to darken cast aluminum, shedding light on its widespread applications. From enhancing aesthetics to improving functionality, darkened cast aluminum is a versatile choice for industrial and residential needs. Combining durability and lightweight versatility, we’ll demonstrate how this material remains an indispensable component in modern manufacturing.
Explore Cast Aluminum Applications With FCC-NA Today!
Why Darken Cast Aluminum?
Darkening cast aluminum can serve both aesthetic and practical purposes. By altering the appearance, you can give the metal a more modern, sleek, or vintage, aged look.
Aesthetic Enhancements
Darkening the raw aluminum can create a more uniform appearance, making it look more sophisticated or industrial, depending on the desired finish. Many people darken aluminum parts in vehicles, machinery, or decorative pieces for a high-end look.
Practical Benefits: Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Darkening aluminum can help improve its corrosion resistance, particularly when the metal undergoes anodization. The darkened surface can also provide a tougher, more durable finish, which is crucial in environments exposed to moisture, heat, and chemicals.
Popular Applications for Darkened Aluminum
Darkened cast aluminum is commonly used in automotive parts, architectural elements, cookware, machinery components, and outdoor furniture. The darkened finish gives these items both functional protection and an attractive look, making them more appealing in various consumer markets.
Understanding the Basics of Darkening Metal Surfaces
When working with metal surfaces, “darkening” refers to processes that result in a darker appearance, often through the creation of an oxide layer, patina, or coatings. These finishes can range from a matte to a glossy shine, depending on the technique.
Oxidation, Patina, and Darkening
Oxidation occurs naturally when aluminum reacts with oxygen in the air, forming a thin oxide layer. According to The Radiation Physics and Chemistry Journal, the oxidation process can also be induced and is the basis for many darkening techniques, as the oxide layer can be manipulated to create various shades. A dark patina is a specific type of oxidation often used in art and design to create an aged, weathered look. Darkening methods are used to visually age aluminum to enhance or control this natural process and achieve the desired outcome.
Differences in Metal Finishes (Matte, Satin, Glossy)
The finish applied to cast aluminum can vary in terms of glossiness. Matte finishes are non-reflective, while satin finishes provide a soft sheen. Glossy finishes offer high reflectivity. The finish chosen will significantly impact both the look and functionality of the final product, affecting everything from aesthetics to cleaning and maintenance. This has been explored significantly in the Journal of Material Science.
Safety Precautions
When darkening cast aluminum with heat, chemicals, or abrasive techniques, safety is paramount. Essential protective gear includes gloves to prevent burns and chemical exposure, safety goggles to protect eyes from chemicals and flying particles, and a respirator when handling dust, fumes, or chemicals. Additionally, ensure proper ventilation in the workspace. Also use a fume extraction system to avoid inhaling harmful fumes, and dispose of chemicals by local environmental regulations to maintain a safe and responsible work environment.
Preparation for Darkening Cast Aluminum
Properly cleaning and preparing the surface of cast aluminum is crucial for achieving a smooth, consistent, and durable darkened finish.
Cleaning the Surface Properly
Proper surface cleaning is essential before darkening cast aluminum to ensure effective treatment and a consistent finish. Cleaning removes dirt, oil, oxidation, and other contaminants that could interfere with the process. Use warm, soapy water to clean off oils and dirt, and for tougher grime, try a degreaser or a baking soda solution. Lane coating highlights that it’s best to avoid harsh chemicals that could damage the surface or impact the final finish, as a clean surface is crucial for achieving a uniform and durable result.
Surface Preparation Techniques
Surface preparation, including glass bead blasting, sanding, or polishing, is essential for achieving a smooth, consistent finish when darkening cast aluminum. Sanding removes thick oxide layers and deep contaminants, while polishing provides a smoother surface but may not remove stubborn impurities. Removing the oxide layer is crucial, as it ensures better adhesion of darkening agents and promotes a more even, durable result.
Techniques to Darken Cast Aluminum
There are several techniques for darkening cast aluminum, including chemical methods, heat treatments, anodizing, and painting, each offering unique benefits for both appearance and durability.
Chemical Methods
Chemical methods for darkening cast aluminum typically involve using aluminum blackening solutions containing chemicals like potassium dichromate or acid-based agents. These solutions applied through spraying or dipping, react with the metal to form a dark oxide layer that provides both aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance. Common oxidizing agents include sulfuric acid (used in anodizing), copper sulfate, and sodium hydroxide, all of which enhance the metal’s durability and appearance.
Heat Treatments
Heat treatments, such as the torch method and oven-based treatments are effective ways to darken cast aluminum by promoting oxidation. The torch method creates varying hues, from brown to aluminum black, depending on the temperature, while oven-based heat treatment offers a more controlled process for an even finish. While these methods are quick and effective, they require precision, as overheating can cause discoloration or damage, and they may not provide the same corrosion resistance as anodizing.
Anodizing Aluminum
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that enhances aluminum’s natural oxide layer, making it more durable and corrosion-resistant while allowing for the application of dyes, such as black, for a darkened finish. There are different anodizing methods, including hard coat anodizing for heavy-duty wear and bright dip anodizing for a smooth, shiny appearance. While anodizing offers superior corrosion resistance and durability, it is more complex and equipment-intensive compared to simpler methods like chemical darkening or painting.
Painting and Coating Options
High-performance paints and coatings like epoxy and polyurethane can be used to darken aluminum while offering protection from the elements, making them ideal for outdoor or industrial use. Powder coating provides a durable, long-lasting finish that resists chipping and fading, making it suitable for items exposed to heavy use. While painting is a quicker and easier method, it may not be as durable as anodizing or other metal finishing techniques, and powder coating, though more durable, tends to be more expensive and time-consuming.
Darkening cast aluminum combines aesthetic enhancement with improved functionality, offering both a sleek appearance and increased durability. Achieving consistent results requires thorough cleaning, precise surface preparation, and adherence to safety protocols. At FCC-NA, we elevate manufacturing with advanced CAE analysis and innovative techniques honed from clutch production expertise. By reducing defects, improving quality, and optimizing processes, we use our Precision Aluminum Casting Technology to deliver lighter, cost-effective products with exceptional finishes, ensuring excellence in every project.
Explore Cast Aluminum Applications With FCC-NA Today!
Step-by-Step Guides for Each Darkening Method

Aluminum’s natural silvery sheen is often enhanced through various darkening techniques, each serving distinct purposes, such as aesthetic enhancement or increased protection. Below are detailed guides for four common methods of darkening aluminum.
Guide to Chemical Darkening
Chemical darkening is a popular method for achieving a darkened finish on aluminum by chemically reacting the metal surface with a solution that alters its color.
- Step 1: Cleaning and Preparing the Surface: Clean aluminum with a mild detergent or degreaser, rinse with water, and use a non-abrasive cloth. For oxidation, lightly sand or apply a chemical cleaner to ensure a contaminant-free surface before finishing.
- Step 2: Applying the Chemical Solution: Use solutions like sulfuric acid, ferric chloride, or potassium dichromate to darken aluminum by forming a dark oxide layer. Apply by brushing, dipping, or spraying, and follow manufacturer instructions to avoid overexposure, which can cause uneven results.
- Step 3: Rinsing and Final Touch-Ups: Rinse aluminum to stop the chemical reaction and stabilize the color. Inspect for inconsistencies and use a fine abrasive pad for touch-ups. Apply a sealer or wax for added protection and durability.
Guide to Heat Treatment Darkening
Heat treatment darkening, also known as heat aging, involves exposing aluminum to controlled temperatures to produce a range of darker shades and increase its mechanical properties.
- Step 1: Preheating the Aluminum Surface: Preheat aluminum to a uniform temperature (250°F to 600°F / 120°C to 315°C) to ensure consistent results and minimize stress.
- Step 2: Applying Controlled Heat: To darken aluminum, heat it in an oven or heat source at the target temperature for 15 minutes to an hour. Monitor closely, as overheating can cause color inconsistencies.
- Step 3: Cooling and Inspecting the Result: Once the desired color is achieved, remove the aluminum and let it cool in open air. Inspect for color evenness and repeat if necessary. Apply a sealant to preserve the finish.
Guide to Anodizing Aluminum
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that thickens the natural oxide layer of aluminum, offering a durable and corrosion-resistant finish while allowing for color customization.
- Step 1: Preparing the Aluminum for Anodizing: Clean aluminum with an alkaline solution or degreaser to remove oils and contaminants. For a matte texture, etch with a mild acid solution for a smooth, even finish.
- Step 2: Setting Up the Anodizing Bath: Mix sulfuric acid with distilled water for the electrolyte bath. Submerge the aluminum, connect it to the positive terminal, and maintain the bath at 18°C to 24°C (65°F to 75°F) with a 15-20V voltage to start anodizing.
- Step 3: Applying the Desired Finish: During anodizing, the aluminum forms a thicker oxide layer, with longer times darkening the color. The shade depends on factors like current, temperature, and time. After anodizing, dye the aluminum and seal it to lock in color and improve corrosion resistance.
Guide to Painting and Coating
Painting or coating aluminum is a common way to darken its appearance while providing additional protection against corrosion.
- Step 1: Surface Preparation for Paint or Coating: Clean aluminum with a degreaser, rinse, and dry. Light sanding with fine-grit sandpaper can create a smooth, matte surface for better coating adhesion.
- Step 2: Choosing the Right Coating Type: Choose from powder coating, spray paint, or liquid coatings. Powder coating is durable, while spray paint suits smaller projects. For darkening, select colors like black or gray, noting that the coating type affects appearance and wear resistance.
- Step 3: Applying and Curing the Paint/Coating: Apply paint or coating evenly using an electrostatic applicator for powder coating or a spray gun/brush for liquid coatings. Cure by baking powder coatings or air drying for paint to ensure a durable, secure finish.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Darkening aluminum can enhance its appearance and durability, but like any metalworking process, challenges may arise.
Problems with Uneven Coloring
The Jalop Journal explores uneven chemical coloring in aluminum, which is often seen in chemical darkening or anodizing processes. It can result from inconsistent application, surface contamination, or variations in the aluminum alloy itself. Causes include uneven application of darkening agents, surface oils or oxidation that prevent proper bonding, and differing metal compositions affecting absorption.
To achieve a uniform finish, thoroughly clean the aluminum with a degreaser, sand the surface lightly, and ensure the even application of the darkening solution. Testing on a small area before full application can also help prevent larger inconsistencies.
How to Fix Surface Flaws
Surface imperfections like scratches, dents, or oxidation can impact the final result of aluminum darkening. These flaws may be caused by pre-existing imperfections or improper handling during the process. To fix these flaws, you can sand minor imperfections with fine-grit sandpaper, polishing afterward to restore smoothness. For deeper scratches or dents, use a metal filler, allowing it to cure before sanding and polishing.
If oxidation is present, remove it with a chemical cleaner or abrasive pad and thoroughly clean the surface afterward to prevent contamination. Proper preparation ensures a smooth, uniform darkening finish.
Dealing with Chemical Reactions
Inconsistent reactions with chemical darkening agents can lead to uneven color or finish on aluminum, often due to variations in alloy composition, solution concentration, temperature, or improper mixing. Alloys with higher silicon or copper may darken unevenly, while incorrect solution strength or temperature can produce inconsistent results.
To address this, understand your aluminum alloy’s properties and test the solution on small aluminum parts first. Ensure correct chemical mixing and maintain the solution’s temperature within the recommended range. Additionally, using protective barriers in harsh chemical environments can help achieve a more uniform reaction.
Aftercare and Maintenance of Darkened Cast Aluminum
Darkening cast aluminum is an effective way to improve its aesthetic appeal and resistance to corrosion. However, maintaining the integrity of the darkened finish is essential to ensure long-lasting durability and visual quality.
Protecting the Darkened Finish
To maintain the darkened appearance of cast aluminum, it’s important to protect the surface from physical damage, moisture, and environmental elements. Applying a clear coat or sealant creates a protective barrier that enhances the finish and provides resistance against scratches, fading, and corrosion. Clear polyurethane, acrylic, or enamel coatings offer durable protection, while specialized sealants can create a hydrophobic barrier for added defense, especially in outdoor or humid environments.
Always ensure the surface is clean and dry before application, and regularly inspect the coating, reapplying as needed to maintain its effectiveness.
Cleaning Darkened Aluminum Surfaces
To maintain the appearance and durability of darkened aluminum, it’s essential to clean it with care. Use mild, non-abrasive cleaners, such as a gentle detergent mixed with warm water, and scrub with a soft cloth or sponge to avoid damaging the finish. Avoid harsh, acidic cleaners and abrasive pads that can scratch or dull the surface. After cleaning, rinse thoroughly to remove any detergent residue. For stubborn marks, consider using a specialized cleaner designed for aluminum to preserve the darkened finish without causing harm.
Reapplying Darkening Treatments Over Time
Over time, the darkened finish on aluminum may fade or wear due to regular use and exposure to environmental elements. To restore the finish, you can reapply darkening treatments. For chemical darkening, clean the surface thoroughly, then reapply the solution evenly, allowing it to cure as per the instructions.
If the aluminum is anodized, the anodizing process can be restored by re-immersing the piece in an anodizing bath to rebuild the aluminum oxide layer. Afterward, sealing with a clear coat or specialized sealant helps protect the new finish. Always consult professional guidance or manufacturer instructions for best results.
Summary
Darkening cast aluminum combines visual enhancement with practical benefits like improved corrosion resistance and durability. Techniques such as chemical treatments, heat application, anodizing, and coatings offer tailored solutions, requiring careful preparation and precision for lasting results.
At FCC-NA, we ensure exceptional quality through an integrated production system, from 3D design to AI-driven analysis and advanced manufacturing. Utilizing technologies like CT scanning and proprietary methods, we achieve zero-defect production and meet stringent specifications for complex components.
Whether enhancing aluminum’s finish or advancing manufacturing precision, FCC-NA has been delivering unparalleled reliability and innovation for over 80 years.
Explore The Benefits of FCC-NA’s Cast Aluminum Applications Today!