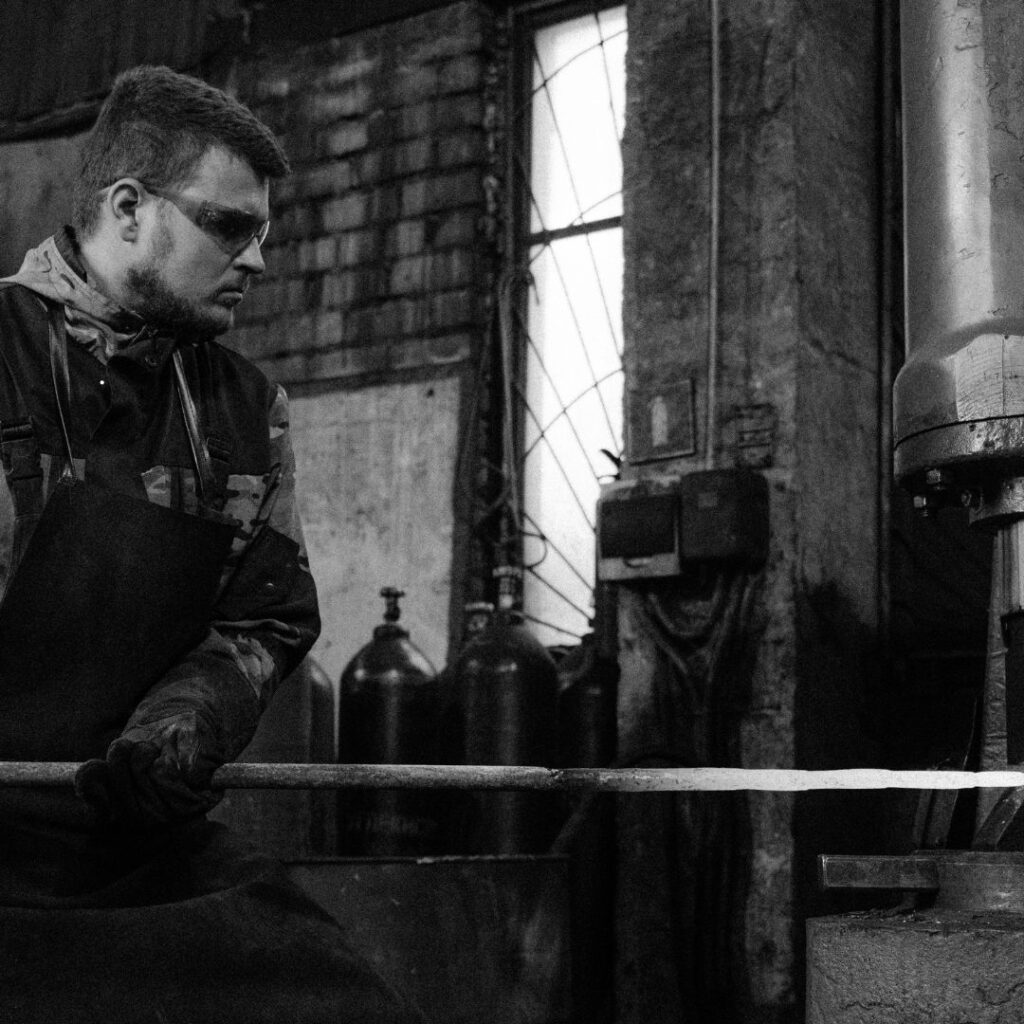
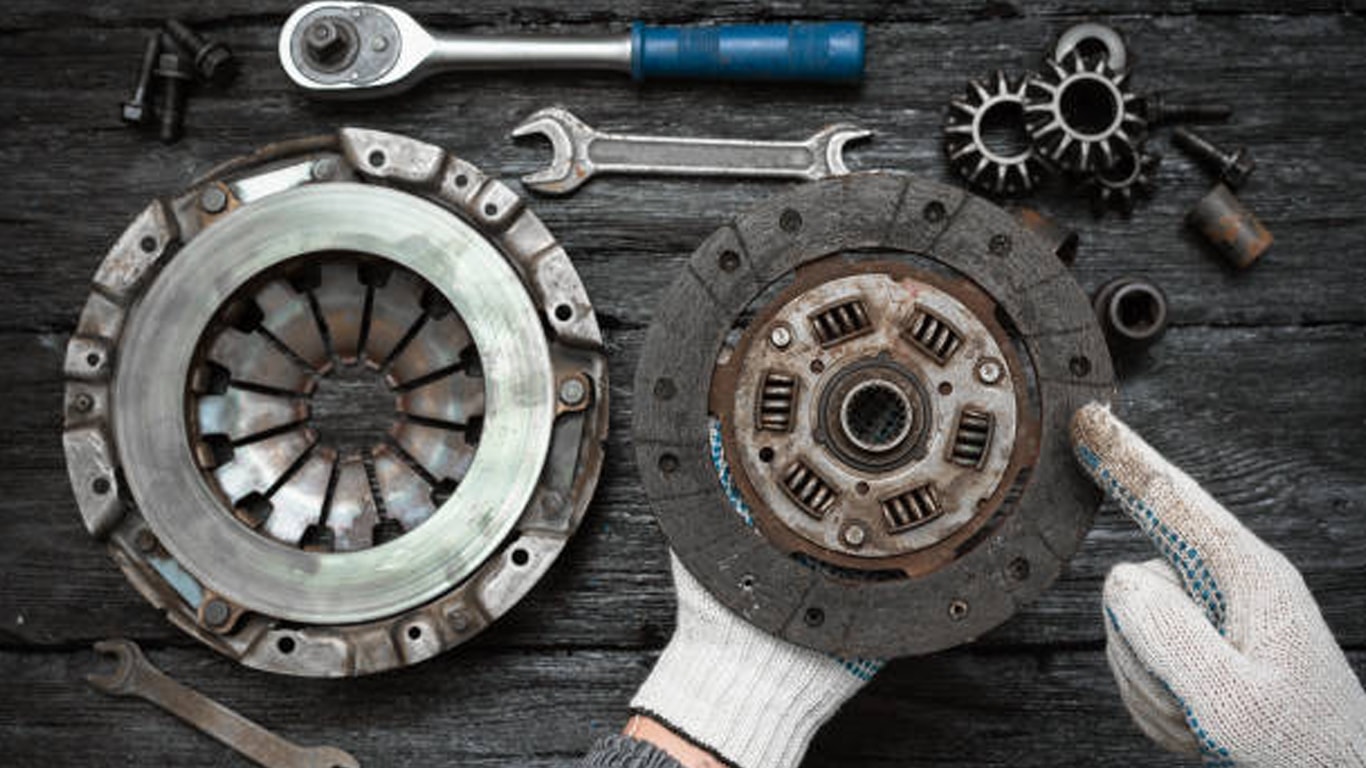
Forging is a time-honored manufacturing process that has evolved significantly over the centuries. From ancient blacksmiths hammering metal by hand to the high-tech forging techniques and engineered metallurgy of today, this process has continuously adapted to meet the demands of modern industry. In this blog, FCC-NA will explore the historical background, traditional methods, and cutting-edge innovations in forging technology that are shaping the future of manufacturing.
Learn More About FCC-NA’s Innovations in Forging Technology Today!
Historical Background and Evolution
Forging dates back to ancient civilizations, where it was used to create tools, weapons, and ornaments. Over the centuries, forging technology has advanced from simple hand tools to complex machinery. The Industrial Revolution marked a significant turning point, introducing steam-powered hammers and automated forging presses that increased production efficiency and precision.
Forging is critical in many industries due to its ability to produce parts with superior mechanical properties. It is commonly used in automotive and transmission equipment, aerospace, defense, and energy sectors. The process ensures high-strength components, reliability, and fatigue resistance, making it ideal for high-performance applications.
Traditional Forging Methods
Traditional forging methods concern various techniques used to shape metal into desired forms. Each method offers unique advantages, depending on the required precision and shape of the final product.
Open Die Forging
This method involves shaping metal between two flat dies, allowing for large and simple shapes. Open Die forging is often used to produce components like shafts and billets. While versatile, it is less precise than other methods and usually requires additional machining.
Closed Die Forging
Also known as impression die forging, closed die forging involves shaping metal within a set of dies that have a specific cavity shape. This method is used to create more complex parts with higher precision and less material waste compared to open-die forging.
Seamless Rolled Ring Forging
Seamless rolled ring forging is used to produce ring-shaped components. The process involves heating a metal billet, punching a hole in the center, and then rolling and deforming the ring to the desired dimensions. The seamless rolled ring forging method is ideal for producing components like flanges and bearings.
Die Casting at FCC-NA has reached new levels of innovations in forging technology with our advanced vacuum die-casting technique, tailored specifically for motorcycle and automotive clutch aluminum parts. This cutting-edge approach boosts casting accuracy while reducing the need for additional machining.
Learn More About FCC-NA’s Innovations in Die Casting Today!
Modern Innovations in Forging Technology
Modern innovations in forging technology have revolutionized the way we produce and manipulate metals, leading to improved efficiency, precision, and material properties.
Advanced Materials
Advanced materials such as superalloys, titanium alloys, and high-strength steels enhance performance and reliability in demanding fields like aerospace, medical implants, and automotive engineering. Superalloys endure extreme temperatures and corrosive environments; titanium alloys combine high strength with low density and corrosion resistance; and high-strength steels offer durability and strength for automotive and structural applications, benefiting from innovations in forging technology and steelmaking.
Precision Forging Techniques
Precision forging techniques, including near-net shape forging, isothermal forging, and cold forging, enhance efficiency, material properties, and precision in producing high-quality components. Near-net shape forging reduces material waste by closely matching the final shape; isothermal forging (a hot forging process) maintains a consistent temperature for better material properties; and cold forging improves mechanical properties and surface finish, especially in small, high-precision parts.
Automation and Robotics in Forging
Automation and robotics in forging, including robotic handling systems, automated forging presses, and smart forging cells, transform the industry by boosting efficiency, precision, and adaptability. Robotic systems streamline material handling, automated presses enhance precision and productivity, and smart forging cells integrate advanced technologies for highly efficient and flexible operations.
Digital Twin and Simulation
Digital twin technology and simulation, including virtual prototyping, process optimization, and predictive maintenance, enhance forging processes by allowing manufacturers to simulate and refine operations before physical production. Virtual prototyping reduces errors and development time, advanced simulations improve process quality and reduce costs, and predictive maintenance uses data analytics to anticipate and prevent equipment failures, minimizing downtime and maintenance expenses.
Additive Manufacturing Integration
Additive manufacturing integration, particularly through hybrid forging and 3D printing, combines traditional forging with 3D printing to produce complex, customized parts while optimizing material use and production efficiency. This hybrid approach enhances design flexibility and leverages the strengths of both techniques to reduce material waste and improve overall production.
FCC-NA has designed our infrastructure to easily scale up for large production runs, resulting in a highly cost-effective system that stands out for its performance and efficiency.
Learn More About FCC-NA’s Innovations in Forging Technology Today!
Environmental and Economic Impacts
Let’s dive deeper into the environmental and economic impacts of modern forging technologies.
Energy Efficiency Improvements
Energy efficiency improvements in forging, through advanced heating techniques like induction heating and energy recovery systems, significantly reduce energy consumption and operational costs while enhancing process sustainability.
Energy efficiency in forging requires smarter, more sustainable practices. By using advanced techniques like induction heating, manufacturers can precisely control temperatures while slashing energy waste. This means lower costs and greater efficiency. On top of that, energy recovery systems capture excess heat and put it back to work, making the entire process more sustainable and eco-friendly.
Waste Reduction Strategies
Waste reduction strategies in forging, including material recycling and process optimization, focus on minimizing waste by recovering scrap metal for reuse and employing advanced techniques to produce components with minimal excess material.
Waste reduction strategies in forging focus on minimizing waste through material recycling and process optimization. By recycling scrap metal directly back into production using cutting-edge technologies like metal shredders, the industry is not only cutting down on waste but also conserving precious resources. With the help of advanced simulation tools and precision forging techniques, manufacturers can achieve near-net-shape production.
This means optimizing die designs and process parameters to minimize excess material from the start, significantly reducing the need for costly post-processing. The result? A more efficient, resource-friendly forging process.
Cost Reduction Methods
Cost reduction methods in forging, such as leveraging economies of scale and efficient resource utilization, aim to decrease per-unit costs and improve overall production efficiency by optimizing resource use and scaling up manufacturing processes.
It’s all about working smarter, not harder. By scaling up production, manufacturers can spread fixed costs across more units, driving down per-unit expenses. Automation and streamlined processes cut labor costs, while optimized energy use and minimal material waste ensure every resource is used to its fullest.
With enhanced process control, the entire FCC-NA operation becomes more efficient, making it possible to produce high-quality, commonly recognized forged products at a lower cost.
Learn More About FCC-NA’s Innovations in Forging Technology Today!
Innovations in Forging Equipment
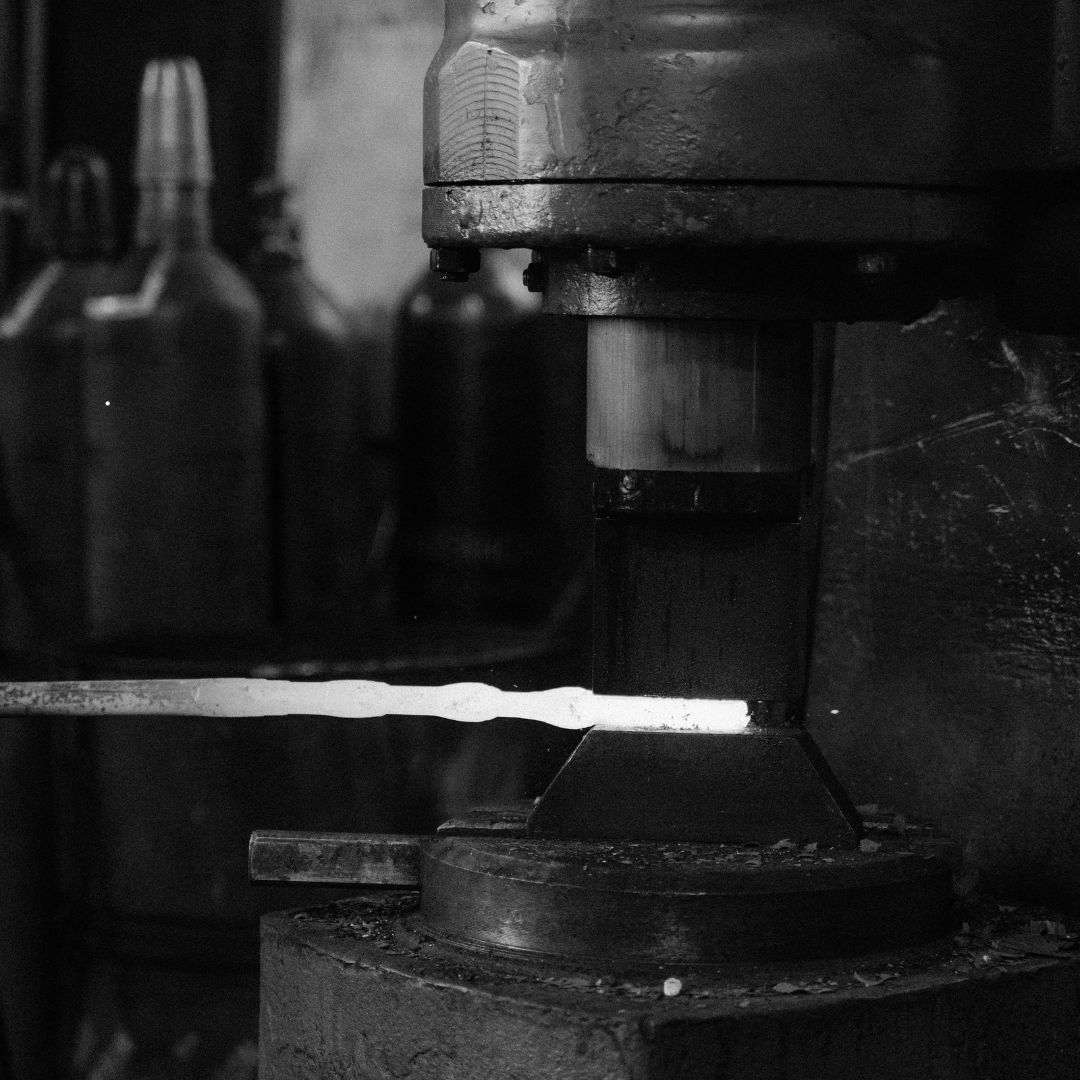

Innovations in forging equipment have significantly advanced the capabilities of manufacturing processes in the metal forging market, improving efficiency, precision, and quality. Here’s a detailed look at some of the key innovations in forging technology equipment.
Advanced Forging Presses
Advanced forging presses, including hydraulic and mechanical presses, enhance forging operations by providing precise control and efficiency, with hydraulic presses offering high tonnage and adaptability, while mechanical presses excel in speed and consistency for high-volume production.
- Hydraulic Presses: Hydraulic presses use fluid power for high-force, precise forging, which makes them ideal for complex tasks requiring uniform force and adaptability. Modern features include programmable control for enhanced precision.
- Mechanical Presses: Mechanical presses rely on mechanical linkages for force, offering speed and efficiency. Innovations in forging technology like servo motors provide precise control, making them perfect for high-volume, fast-cycle manufacturing.
Induction Heating Systems
Induction heating is a non-contact method of heating metals using electromagnetic fields. Induction heating systems offer numerous advantages, making them essential for modern forging applications.
Key benefits include:
- Energy Efficiency: Induction heating is highly efficient, as it directly heats the material with minimal energy loss. This reduces the overall energy consumption compared to traditional heating methods.
- Precise Control: The process offers precise control over temperature, which is critical for achieving the desired material properties and consistency.
- Reduced Heating Time: Induction heating provides rapid heating, which speeds up the forging process and improves production rates.
- Localized Heating: It allows for targeted heating, which can reduce the thermal impact on surrounding areas and enhance the quality of the forged components.
Induction heating is widely applied in modern forging for pre-heating materials to optimal temperatures, post-heating to achieve desired material properties through controlled heating and cooling, and selective heating to target specific areas, enhancing precision and reducing waste.
Sensor Technology and Monitoring
Sensor technology and monitoring in forging enhance production quality and reduce downtime by utilizing real-time data acquisition and condition monitoring systems. Advanced sensors capture variables like temperature and pressure, allowing for immediate process adjustments.
Condition monitoring systems continuously assess the health and performance of forging equipment, enabling predictive maintenance to prevent failures, tracking performance trends to address efficiency issues, and providing real-time alerts for immediate corrective actions, reducing downtime and enhancing equipment lifespan.
At FCC-NA, our extensive experience in precision equipment allows us to excel in single-shot forming. This expertise in press forming technology not only helps in producing lighter critical components but also optimizes processes for near-net-shape production, driving significant cost savings.
Learn More About FCC-NA’s Press Forming Technology Today!
Industry 4.0 and Forging
Industry 4.0 is transforming manufacturing by weaving digital technologies into every step of the process. This revolution is creating smarter, more efficient, and highly adaptable production environments that redefine what’s possible in modern manufacturing.
IoT in Forging Operations
The Internet of Things (IoT) transforms forging operations by connecting equipment to a network for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Sensors collect and transmit data on key parameters like temperature and pressure, allowing for immediate adjustments and enhanced process control. IoT devices also track equipment conditions, enabling proactive maintenance that prevents unexpected breakdowns and reduces downtime.
IoT facilitates data-driven decision-making in forging by providing real-time insights into operational performance, enabling enhanced process control for improved product quality and consistency. Additionally, data analysis helps optimize processes, boosting operational efficiency by reducing waste and energy consumption.
Big Data and Analytics
Big data and analytics enhance forging operations by leveraging process data analysis for pattern recognition, optimization, and quality control. They enable predictive insights for anticipating quality issues and automating quality checks through sensor integration, leading to better product quality and operational performance.
Cybersecurity in Forging
As forging operations become more digital, cybersecurity is crucial for protecting intellectual property and ensuring operational security. Key strategies include access controls, encryption to safeguard sensitive data, network security measures like firewalls and intrusion detection, and robust incident response plans to mitigate cyber threats and breaches.
At FCC-NA, we’re dedicated to pushing the boundaries of product development and manufacturing. Our commitment is to not just meet but surpass our customers’ expectations across all fronts: Safety, Quality, Cost, and Delivery.
Learn More About FCC-NA’s Innovations in Forging Technology Today!
Future Trends in Forging Technology
Future trends in forging technology are set to revolutionize the industry by emphasizing sustainability, advanced lightweight materials, and customization.
Sustainable Forging Practices
Sustainable forging practices are evolving through the use of eco-friendly materials like recycled metals and sustainable alloys, alongside green manufacturing techniques that emphasize energy efficiency and waste minimization. These approaches reduce environmental impact by lowering reliance on raw materials, enhancing energy efficiency, and minimizing waste through advanced forging methods.
Innovations in Die Technology
Innovations in die technology, including advanced die materials and rapid die manufacturing techniques, are transforming the forging industry by improving die performance, extending lifespans, and enabling faster, more flexible production. High-performance alloys and coatings enhance die durability, while additive manufacturing and digital and computer-aided design tools accelerate and optimize the die creation process, allowing for rapid prototyping and customization.
Customized Forging Solutions
Customized forging solutions, driven by on-demand manufacturing and personalized forging designs, enhance flexibility, reduce inventory, and produce tailored components that meet specific customer needs and industry standards. On-demand manufacturing minimizes storage costs and allows quick adaptation to market changes, while advanced technologies enable the creation of bespoke components, particularly valuable in various industries requiring specialized forged parts.
Conclusion
The forging industry has seen remarkable advancements that enhance efficiency, precision, and sustainability.
At FCC-NA, we’re shaping the future of forging with a focus on sustainability, cutting-edge technology, and tailored solutions. Our innovations are setting the stage for a new era in clutch manufacturing—one where efficiency, precision, and environmental responsibility go hand in hand. As we advance, FCC-NA is leading the charge in making “Forging” a pivotal force in the ever-evolving world of modern manufacturing to meet specific product requirements.
Learn More About FCC-NA’s Innovations in Forging Technology Today!