The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) describes the integration of interconnected sensors, instruments, and smart devices within industrial environments. These “things” enable decision-makers like FCC to collect, exchange, and analyze data to drive smarter, for a more efficient manufacturing process. Unlike consumer IoT, which focuses on enhancing daily life activities, IIoT targets industrial sectors such as manufacturing, energy, healthcare, and transportation. It leverages technologies like machine learning, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics to optimize operations, improve productivity, and facilitate predictive maintenance.
In this article, we will try to break down what it means to leverage to tools of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). FCC is constantly working to create innovative core technologies and products that better serve the needs and requirements of industrial companies and a growing customer base. In this regard, we assiduously leverage the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) to improve on our clutch technological developments.
Explore Our Tech And Development Facilitated By IIoT Devices!
Evolution of IIoT
The concept of connecting machines isn’t entirely new. However, the recent advancements in several key areas have fueled the significant growth and transformative potential of IIoT:
- Sensors and Embedded Systems: Smaller, cheaper, and more powerful sensors allow for collecting detailed data from various aspects of industrial processes.
- Connectivity: Improved network infrastructure like 5G and IoT-specific protocols enable faster and more reliable data transfer.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud platforms like AWS and Microsft Azure offer scalable data storage, processing power, and tools for analyzing vast amounts of data generated by IIoT devices.
- Analytics and AI: Advanced analytics and artificial intelligence algorithms help glean valuable insights from data, leading to more informed decision-making and automation.
Importance in Modern Industry
IIoT plays a pivotal role in modernizing industrial operations and addressing key challenges faced by businesses. Some of these are increasing competition, fluctuating market demands, and rising operational costs. By connecting machines, devices, and systems, IIoT enables real-time visibility into operations which then allows proactive decision-making and rapid response to issues.
Based on a study conducted by Tidio it was found that 83% of companies are already using AI to make strategic decisions. It has been found that it facilitates the transition from reactive to predictive maintenance strategies, reducing downtime and prolonging asset lifespan. Moreover, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) fosters collaboration across departments and enhances communication between stakeholders, leading to improved efficiency and agility through smart and connected devices.
As industries continue to embrace digital transformation, IIoT will remain a driving force behind innovation, enabling organizations to unlock new opportunities and achieve sustainable growth.
Key Components of IIoT
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) systems, enable organizations to harness the power of data-driven insights to optimize operations, improve efficiency, and drive innovation in industrial settings. Here are a few ways they accomplish this.
Sensors and Actuators
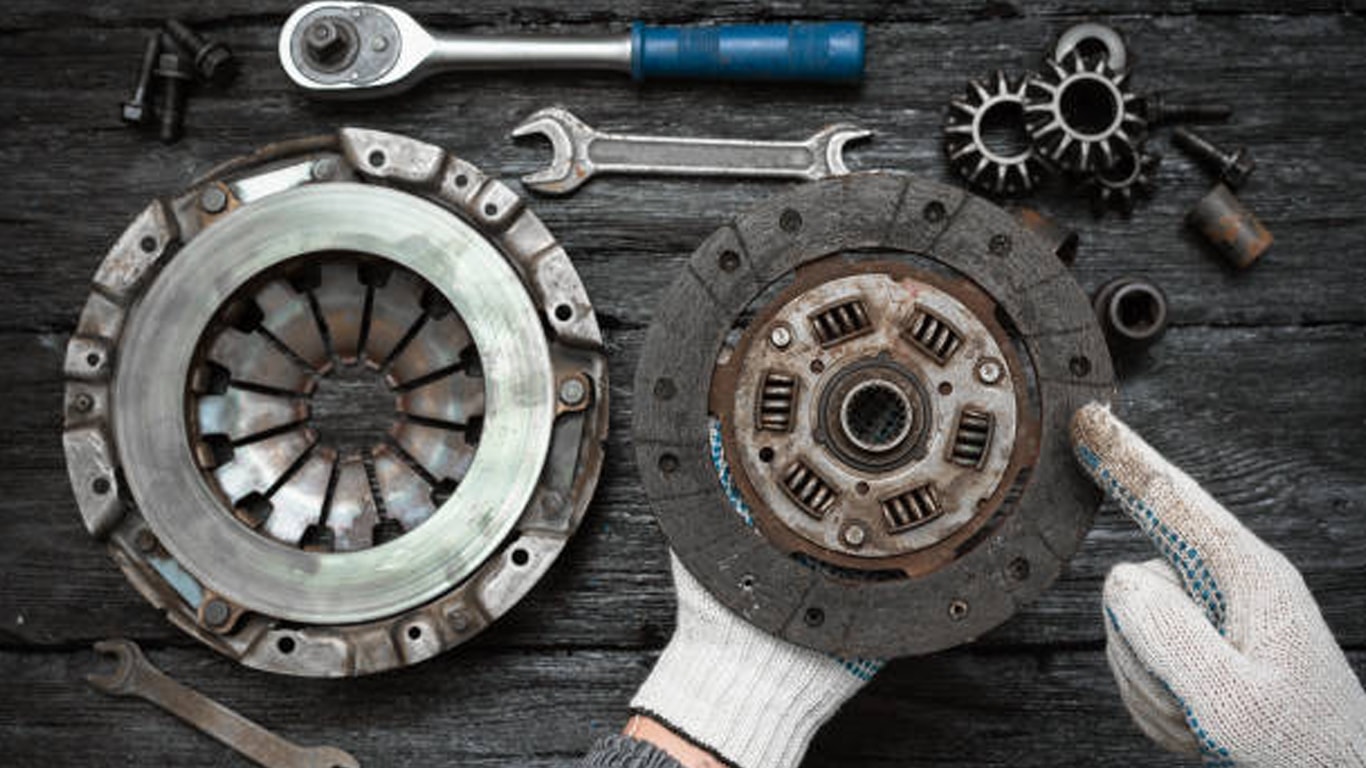
Sensors are fundamental components of IIoT systems, responsible for capturing data from the physical environment. These devices can measure various parameters such as temperature, pressure, humidity, vibration, and more. Actuators are used to control physical processes based on the data collected by sensors. The clutch actuator for instance helps the driver to control the interruption of power. Together, sensors and actuators enable real-time monitoring and control of physical and digital components of industrial assets, providing valuable insights into equipment performance, environmental conditions, and operational efficiency.
Because the clutch actuator relies on friction to transmit torque, when the load in the drive train surpasses the torque limit that friction can handle, the clutch’s driving and driven components will slip automatically. This slipping action serves to prevent overload in the drive system. FCC has made it our point of duty to ensure that the data harnessed from the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) devices are the basis on which we improve our friction material.
Learn More About The Research And Development Of FCC Friction Material!
Connectivity Solutions
Connectivity solutions form the backbone of IIoT infrastructure, enabling seamless communication between devices, sensors, your data center, and backend systems. Various technologies are utilized for this purpose, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, cellular networks (3G/4G/5G), Ethernet, and LPWAN (Low-Power Wide-Area Network). The choice of connectivity solution depends on factors such as range, bandwidth, power consumption, and security requirements. These technologies facilitate data transmission from edge devices to centralized data repositories for further analysis and decision-making.
Edge Computing
Edge computing is the processing and analysis of data closer to its source. This is typically at or near the device or sensor level, rather than relying solely on centralized cloud infrastructure. This approach offers several advantages for IIoT applications, including reduced latency, improved reliability, and enhanced data privacy. By performing data processing tasks locally, edge computing minimizes the need for continuous high-bandwidth communication with cloud servers. This makes it ideal for use cases where real-time responsiveness is critical for server and application protection and enables predictive maintenance, quality control, and safety monitoring.
Cloud Platforms
Cloud platforms like Plex Systems serve as centralized hubs for storing, processing, and analyzing large volumes of data generated by IIoT devices and sensors. These platforms offer scalable computing resources, advanced analytics capabilities, and integration with other enterprise systems. Cloud-based IIoT solutions enable organizations to leverage machine learning algorithms, predictive analytics, and data visualization tools to extract actionable insights from their data. It was found that 74% of enterprises rely on one cloud platform or another as a solution to workload management. Even then, more businesses are opting for a multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategy, rather than solely relying on either a public or private cloud approach.
Cloud platforms also facilitate remote monitoring, management, and configuration of IIoT deployments across distributed locations. Additionally, cloud platforms provide robust cyber-security features to safeguard sensitive data and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Fcc relies on Plex Systems to connect our people, as well as collect data, to automate, track, and analyze the operations of our systems, machines, and supply chains. Without a cloud platform, we would not be able to operate on the large scale that we do. Operating for over 80 years with over 29 strategically located global manufacturing facilities we can pour our energies into developing our core technologies and products.
Learn More About FCC Operations!
Applications Across Industries

IIoT offers transformative benefits across industries, empowering organizations to drive innovation, improve efficiency, and deliver enhanced value to customers and stakeholders. Let’s take a deeper look at a few of these industries and industrial applications.
Manufacturing Sector
IIoT revolutionizes the manufacturing sector by optimizing production processes, enhancing quality control, and enabling predictive maintenance. Manufacturers like FCC, utilize IIoT-enabled sensors to monitor manufacturing equipment and health, track inventory in real-time, and automate production workflows. Predictive analytics algorithms analyze machine data to predict potential failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and reducing maintenance costs. Additionally, IIoT facilitates the implementation of smart factories, where interconnected machines and systems communicate seamlessly to improve efficiency, productivity, and overall operational performance.
Energy and Utilities
In the energy and utilities sector, IIoT plays a crucial role in optimizing energy production, distribution, and consumption. Smart grid technologies leverage IIoT-enabled sensors to monitor power generation, transmission, and distribution networks in real time. This data enables utilities to improve grid reliability, reduce energy losses, and optimize load balancing.
IIoT also facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, by providing insights into energy generation patterns and optimizing resource utilization. Furthermore, IIoT enables the implementation of smart metering systems, empowering consumers to monitor their energy usage and make informed decisions to reduce consumption and lower costs.
Transportation and Logistics
IIoT transforms the transportation and logistics industry by enhancing fleet management, improving asset tracking, and optimizing supply chain operations. Fleet operators utilize IIoT-enabled telematics devices to monitor vehicle performance, track location in real time, and optimize routes for fuel efficiency and on-time delivery. In warehousing and distribution centers, IIoT sensors enable real-time inventory tracking, warehouse automation, and predictive maintenance of equipment such as conveyor belts and forklifts. Additionally, IIoT-powered logistics platforms provide end-to-end visibility into supply chain processes, enabling proactive decision-making, risk mitigation, and customer service improvements.
Healthcare Industry
In the healthcare industry, IIoT facilitates remote patient monitoring, personalized treatment, and operational efficiency improvements. Wearable devices equipped with biometric sensors enable continuous monitoring of patient vital signs, allowing healthcare providers to remotely track patient health metrics and detect early warning signs of potential health issues. IIoT-enabled medical devices, such as smart infusion pumps and connected implants, enhance patient safety and medication adherence. Furthermore, IIoT supports hospital operations by optimizing asset management, improving workflow efficiency, and reducing equipment downtime through predictive maintenance solutions.
Advantages of IIoT Adoption
IIoT adoption offers numerous advantages. By harnessing the power of real-time data insights and automation, organizations can optimize operational technology, mitigate risks, and achieve sustainable growth in today’s dynamic industrial landscape.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
IIoT adoption leads to increased efficiency and productivity by streamlining processes, automating tasks, and optimizing resource utilization. Real-time data insights provided by IIoT sensors enable organizations to identify bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and improve operational efficiency. By monitoring equipment performance and production metrics in real time, IIoT helps identify inefficiencies and enables proactive decision-making to maximize productivity.
Cost Reductions and Resource Optimization
IIoT enables cost reductions and resource optimization by minimizing waste, reducing energy consumption, and optimizing asset utilization. Real-time monitoring of equipment health and performance allows for predictive maintenance, preventing costly unplanned downtime and reducing maintenance expenses. IIoT-driven automation streamlines operations reduces manual labor costs, and improves overall resource efficiency.
Enhanced Safety Measures
IIoT adoption enhances safety measures in industrial environments by providing real-time monitoring and alerts for potential hazards. IIoT sensors can detect abnormal conditions, such as equipment malfunctions or environmental hazards, and trigger immediate alerts to operators or automatically shut down operations to prevent accidents. By improving situational awareness and facilitating timely responses to safety incidents, IIoT helps minimize risks and protect the well-being of workers.
Predictive Maintenance
IIoT enables predictive maintenance strategies and effective risk management by continuously monitoring equipment health and performance using sensors and predictive analytics. By analyzing data on factors such as temperature, vibration, and usage patterns, IIoT systems can predict when equipment is likely to fail and schedule maintenance proactively. This approach minimizes downtime, reduces maintenance costs, and extends the lifespan of critical assets, ultimately improving overall operational efficiency.
Emerging Trends in IIoT
Emerging trends in IIoT are poised to reshape industrial operations, driving innovation, efficiency, and competitiveness across various sectors. Let’s explore a few.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Integration of AI and machine learning into IIoT systems is a significant trend that enables more advanced data analytics and decision-making capabilities. By leveraging AI algorithms, IIoT platforms can analyze vast amounts of sensor data in real time, uncovering valuable insights and patterns in raw data that humans might overlook. AI-driven predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, and optimization algorithms help organizations improve operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and enhance overall performance.
Blockchain Applications
Blockchain technology is increasingly being explored for its potential applications in IIoT, particularly in areas such as supply chain management, asset tracking, and data security. By providing a decentralized and immutable ledger, blockchain technology enhances transparency, traceability, and trust in IIoT ecosystems. Smart contracts enable automated and tamper-proof execution of agreements between parties, facilitating seamless transactions and ensuring compliance with contractual obligations.
5G Connectivity
The rollout of 5G networks represents a significant advancement in IIoT connectivity for industrial devices, offering higher bandwidth, lower latency, and increased reliability compared to previous generations of wireless technology. 5G enables real-time data transmission and processing, supporting applications such as autonomous vehicles, remote monitoring, and augmented reality in industrial environments. The high-speed and low-latency nature of 5G connectivity unlocks new possibilities for IIoT deployments, driving innovation and enhancing operational efficiency.
Edge AI
Edge AI refers to the integration of artificial intelligence algorithms and machine learning models directly into edge devices, such as sensors, gateways, and controllers, enabling real-time data processing and decision-making at the network edge. By deploying AI inference capabilities closer to the data source, organizations can reduce latency, minimize bandwidth requirements, and enhance data privacy and the security operations center. Edge AI enables autonomous operation, intelligent monitoring, and adaptive control of internet-connected devices in IIoT applications, empowering organizations to achieve greater efficiency and responsiveness in dynamic industrial environments.
Summary
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) represents a transformative force in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, offering immense opportunities for organizations to drive efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness in today’s digital economy. By embracing IIoT technologies and best practices, organizations can navigate the complexities of the modern industrial landscape and emerge as leaders in their respective industries.
At FCC, we adopt a thorough and progressive approach to developing and manufacturing our products. This includes integrating the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) into day-to-day operations and manufacturing processes. Our dedication is unwavering as we strive to surpass our customers’ expectations in safety, quality, cost-effectiveness, and timely delivery.
Explore Our Tech And Development Facilitated By IIoT Devices!