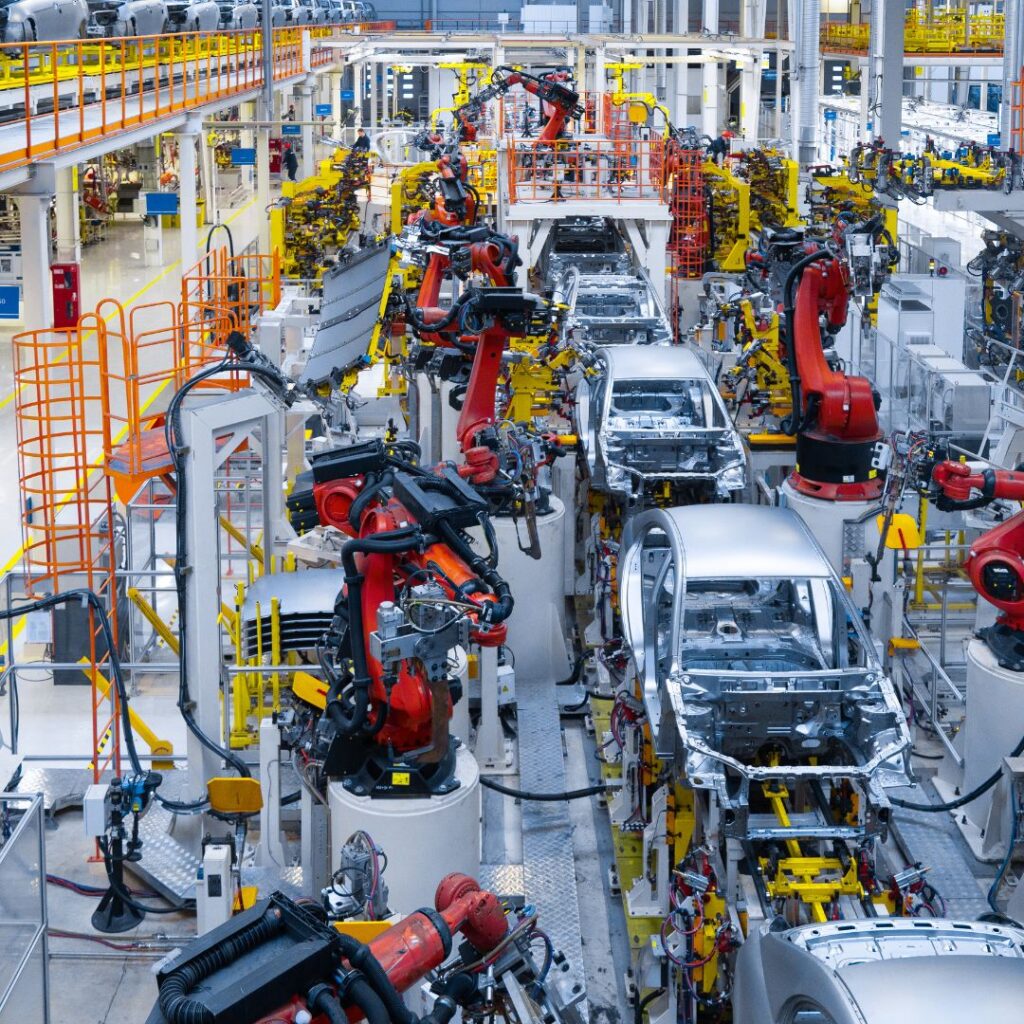
The assembly line, a revolutionary concept in the manufacturing industry, has transformed the landscape of production practices worldwide. It has provided a robust platform for major industries, notably in the automotive sector, to enhance efficiency, increase productivity, and deliver unmatched quality.
FCC, with its eight-decade-long legacy in the automotive industry, stands testament to this evolution. A surprising statistic to underline the impact of these changes is that today, every 20 seconds, a new automobile rolls off an assembly line in the UK. This striking figure underlines the power of assembly line best practices in driving operational excellence and product quality.
In this post, let’s explore the top assembly line best practices.
What is Assembly Line Production?
Assembly line production is a manufacturing methodology that emphasizes the sequential performance of tasks. Each workstation contributes to the final product by executing a specific operation. This systematic flow of the product through various stages of production, where each stage builds upon the previous, results in significant time savings and increased output.
The evolution of assembly line production is fascinating. It dates back to the early 20th century, when the automotive industry pioneer, Henry Ford, introduced the concept to optimize the production of his Model T cars. This revolutionary method allowed for more vehicles to be produced in less time, reducing costs and making automobiles more accessible to the masses.
Since Ford’s era, assembly line production has evolved considerably, with advancements in technology introducing automated processes, robotics, and computer-controlled systems. These innovations have not only sped up production but also increased accuracy and reduced human error. Today, companies like FCC continue to push the boundaries of assembly line production, leveraging their core capabilities to maximize the safety, quality, cost, and delivery of their products.
The Importance of Assembly Line Production and Benefits of Mastering Its Art
Mastering the art of assembly line best practices is a must in modern manufacturing for a myriad of reasons.
Maximizes Efficiency
Through the division and distribution of labor among different workstations, assembly lines ensure that no time is wasted in moving workers or tools unnecessarily. This streamlining significantly reduces production time and costs, leading to increased output and profitability.
Elevates the Quality of Production
Each task within an assembly line is handled by specialists trained in their respective roles. This specialization fosters an environment of excellence and precision, thereby enhancing the overall quality of the end product.
Increases Scalability and Adaptability
Lastly, mastering assembly line best practices introduces a level of scalability and adaptability that can be transformative for a business. As market demand fluctuates, assembly lines can be easily scaled up or down, ensuring optimal resource utilization at all times. This flexibility to respond swiftly to market dynamics is a crucial competitive advantage in today’s volatile business landscape.
Principles of Assembly Line Design
An understanding of the principles of assembly line design is fundamental to truly grasping the art of assembly line best practices. Two key principles that lay the groundwork for a successful assembly line are line balancing and workstation layout optimization.
Line Balancing
Line balancing is a production strategy that involves allocating work to different stations in a line to optimize output and minimize idle time. This method ensures that every workstation has an equal amount of work, thereby preventing any bottlenecks or delays in the production process. Studies reveal that effective line balancing can significantly enhance assembly line efficiency and throughput.
Workstation Layout Optimization
Workstation layout optimization refers to the strategic arrangement of workstations in a manner that maximizes efficiency and minimizes movement and waste. This could involve placing related tasks close together, arranging tools in order of use, or just creating a more ergonomic workspace. An optimized workstation layout can lead to better productivity, less worker fatigue, and increased product quality.
Key Components of an Assembly Line
Taking a step further into the mechanics of an assembly line, let’s delve into the integral components that bolster its efficiency and productivity. These key elements, which are the bedrock of modern assembly lines, include conveyor systems, Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), and robotics integration.
Conveyor Systems
Conveyor systems encompass a variety of mechanisms that facilitate the movement of items through an assembly line. They serve as the lifeline of an industrial assembly line, driving its speed and efficiency. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global conveyor system market size is expected to reach USD 10.6 billion by 2025. This growth signifies the increasing reliance on conveyor systems in industries, including automotive manufacturing. Their ability to handle bulky materials over long distances, combined with their adaptability to varying production needs, makes conveyor systems an indispensable asset in assembly line production.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), another essential component of modern assembly lines, are mobile robots that follow markers or wires in the floor or use vision, magnets, or lasers for navigation. They are used for transporting raw materials, components, and finished products, ensuring a smooth and consistent flow of goods throughout the production process. Studies highlight that the use of AGVs leads to increased operational efficiency, reduced labor costs, and improved safety.
Robotics Integration
Lastly, the integration of robotics in assembly lines has ushered in a new era of precision and efficiency in manufacturing. Robotic systems are capable of executing complex tasks with high precision and speed, reducing human error and increasing productivity. According to Wevolver, the adoption of robotics in industries could boost productivity by up to 60%, underscoring the transformative potential of robotics integration in assembly line production.
Human Factors in Assembly Line Efficiency
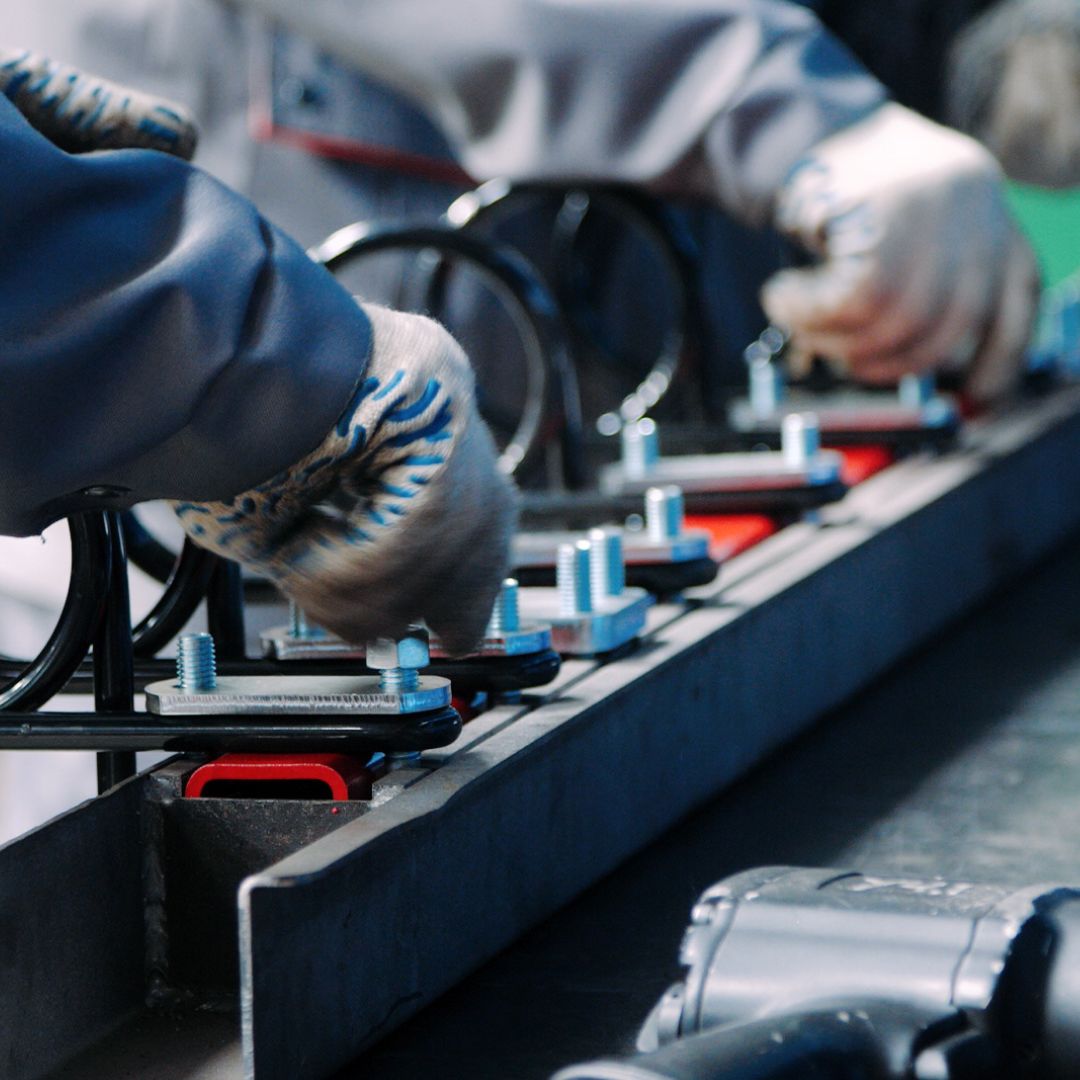

Despite the significant role of machinery and technology in assembly line production, we must acknowledge that human factors underpin the overall efficiency and success of assembly lines. Taking care of the workforce’s well-being and professional development remains a top priority for world-class organizations.
Ergonomics and Worker Safety
Ergonomics, the study of people’s efficiency in their working environment, plays a fundamental role in assembly line production. A well-designed ergonomic environment not only boosts worker productivity but also significantly mitigates the risk of work-related injuries. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, implementing ergonomics can lead to a reduction in musculoskeletal disorders, one of the leading causes of work-related absences. Therefore, ensuring ergonomic workstations and safe working conditions translates into a healthier, more productive workforce, and by extension, an effective and efficient assembly line.
Training and Skill Development
Training and skill development are equally pivotal in enhancing assembly line efficiency. A well-trained workforce not only performs tasks more proficiently but also adapts more quickly to changes in assembly line processes or technologies. Harvard Business Review underscores the importance of continuous training, noting that it facilitates workforce adaptability, particularly in the face of rapidly evolving industry trends and technologies. Thus, investing in employee training and skill development not only lends to improved production standards but also fosters a culture of continuous learning and adaptability that can help organizations remain competitive in today’s dynamic market landscape.
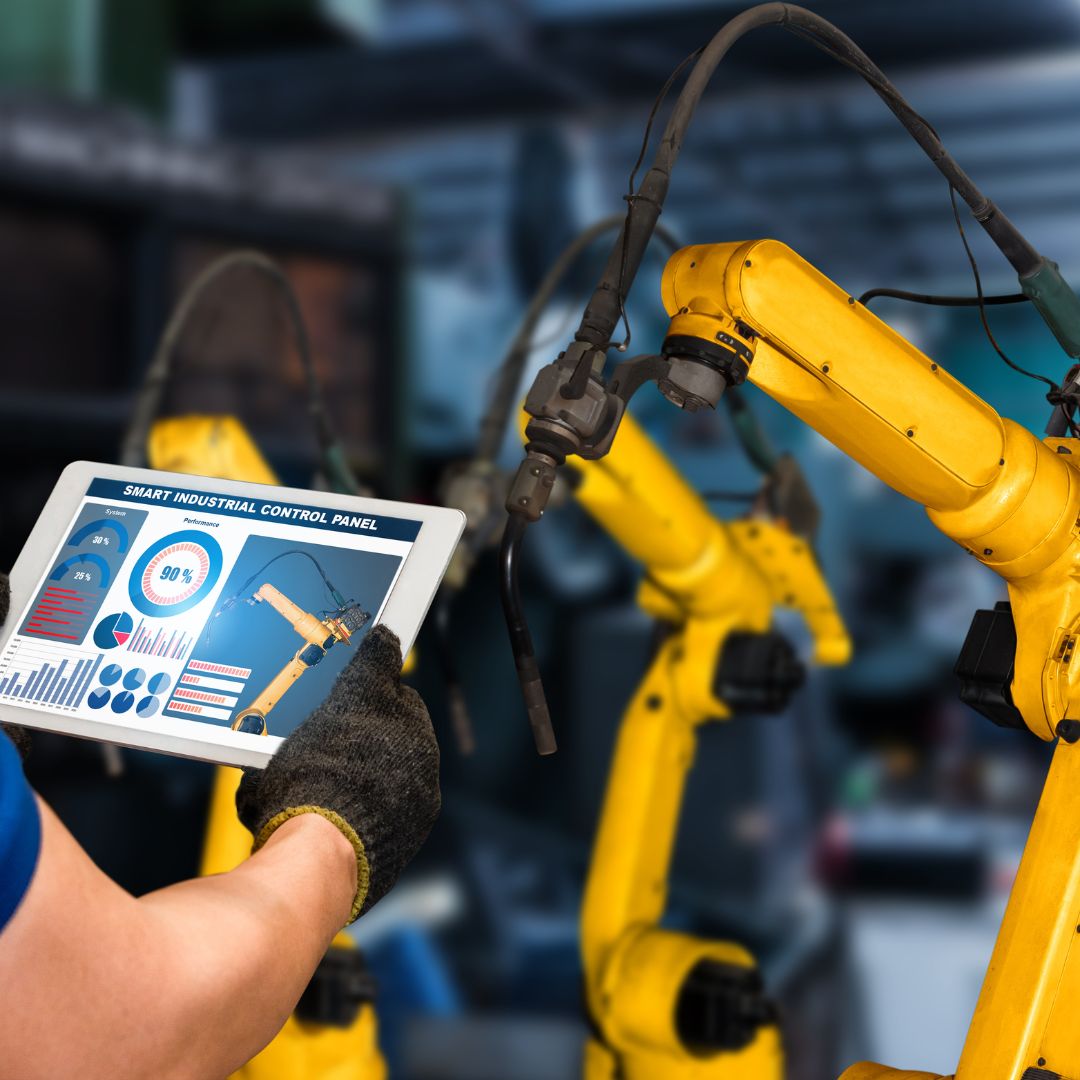
Technology and Industry 4.0
As we delve deeper into the era of Industry 4.0, it’s clear that technology is not only transforming but also redefining assembly line best practices. Two key elements at the heart of this technological revolution are the Internet of Things (IoT) and Data Analytics.
IoT in Assembly Line Monitoring
The Internet of Things (IoT) has immense potential to optimize and enhance assembly line monitoring. IoT devices, embedded with sensors and software, can collect and exchange real-time data, enabling continuous monitoring and predictive maintenance of machinery. With IoT, it is possible to predict and prevent equipment failure, thereby reducing downtime and enhancing overall production efficiency. A study by Deloitte highlights that using IoT for predictive maintenance can reduce maintenance costs by 12%, reduce downtime by 18%, and extend the life of the machinery by 20%.
Data Analytics for Continuous Improvement
Furthermore, the advent of sophisticated data analytics tools has opened up new avenues for continuous improvement in assembly line production. These tools enable manufacturers to analyze vast volumes of data generated by assembly lines, uncovering insights that can help optimize production processes, boost efficiency, and reduce waste. For example, data analytics can identify patterns and trends in production that may indicate potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies, enabling proactive intervention to resolve issues before they escalate. A report by McKinsey shows that companies using data analytics in manufacturing have observed a 50% decrease in product defects, along with a considerable reduction in downtime. This illustrates the power of data analytics in driving continuous improvement in assembly line production.
Achieving Quality Control
In the pursuit of assembly line excellence, one cannot overlook the paramount importance of quality control in modern manufacturing. It ensures the product meets the designated specifications and customer expectations, thereby upholding the brand’s credibility and customer satisfaction.
Inspection Points
Inspection points are strategically set up in various segments of the assembly line to scrutinize the quality of the product’s components and the assembly process itself. Each inspection point serves as a checkpoint to detect and rectify errors or defects immediately, ensuring that only quality products move to subsequent stages of the production line. Overall, in-line inspection points significantly reduce production errors and enhance overall process efficiency.
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a method used to analyze and control production processes using statistical methods. SPC employs statistical tools to inspect a sample of product output and determine whether the process is functioning within its set parameters. If deviations are identified, corrective actions are taken promptly, thereby reducing waste and increasing productivity. According to the American Society for Quality, the application of SPC in manufacturing results in higher quality products, improved customer satisfaction, and reduced waste and rework. Its implementation fosters a culture of continuous improvement, essential for the success of an assembly line operation.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of assembly line best practices necessitates a multi-faceted approach. From investing in continuous training and skill development, harnessing the potential of technology and Industry 4.0, implementing inspection points, to utilizing statistical process control, each aspect plays a vital role in enhancing efficiency and achieving superior quality control.
Looking toward the future, the landscape of assembly line production will continue to evolve with advancements in technology and innovation. The integration of artificial intelligence and robotics, coupled with advanced analytics, will pave the way for smart factories where automation and data exchange will lead to unprecedented levels of efficiency and customization.
At FCC, we stay at the forefront of these innovations, leveraging our expertise to enhance assembly line production for our automotive and motorcycle customers. Interested in discovering how you can benefit from our advanced solutions? Get in touch with us today and let’s drive the future of assembly line production together.