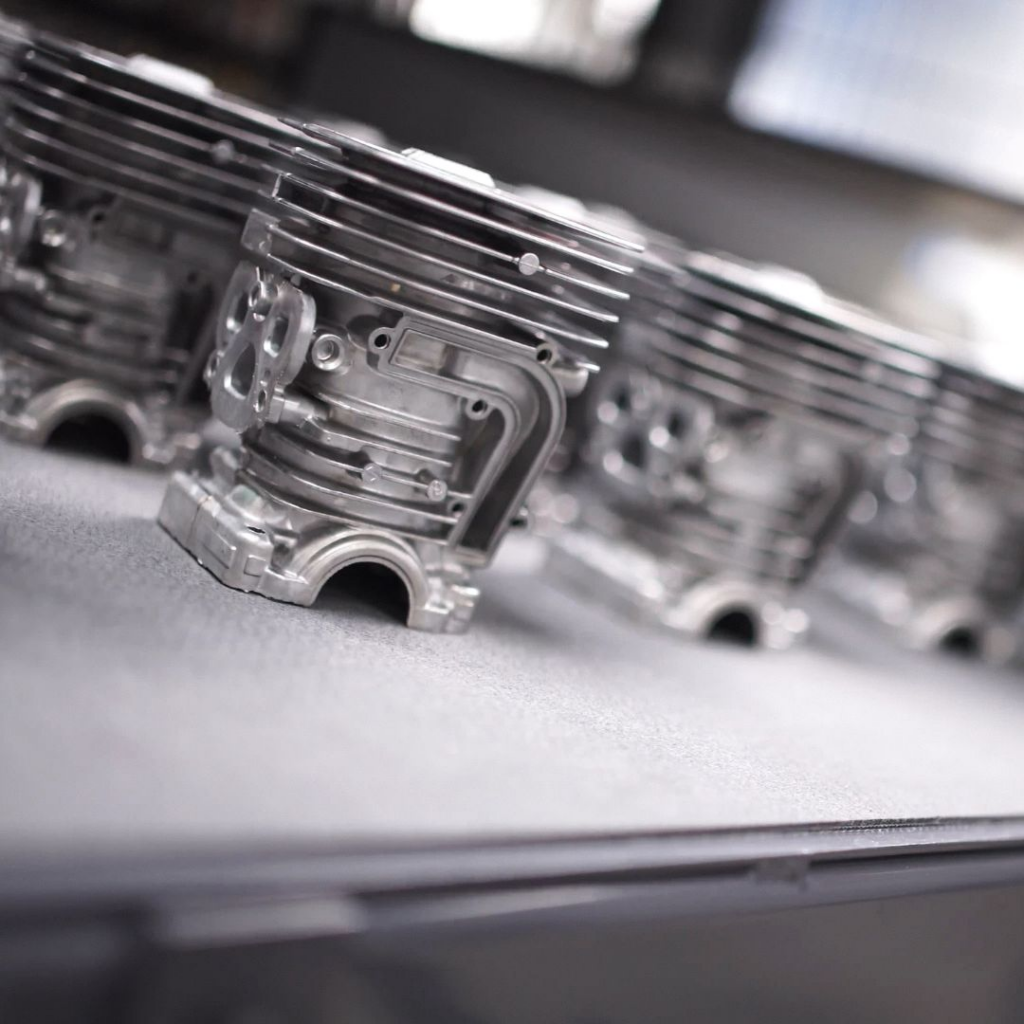
Aluminum casting, a process dating back to 1807 in England, has evolved into a crucial component of modern manufacturing. This method of forming aluminum into a variety of complex shapes has bolstered advancements in numerous industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics, by providing lightweight, durable, and cost-effective solutions. Given its importance, mastering the art and science of quality control in aluminum castings is essential for manufacturers aiming to meet rigorous standards and deliver superior products.
In this blog post, we will explore the evolution of aluminum casting techniques, underscore its pivotal role in today’s manufacturing landscape, and provide a thorough walkthrough on implementing effective quality control measures.
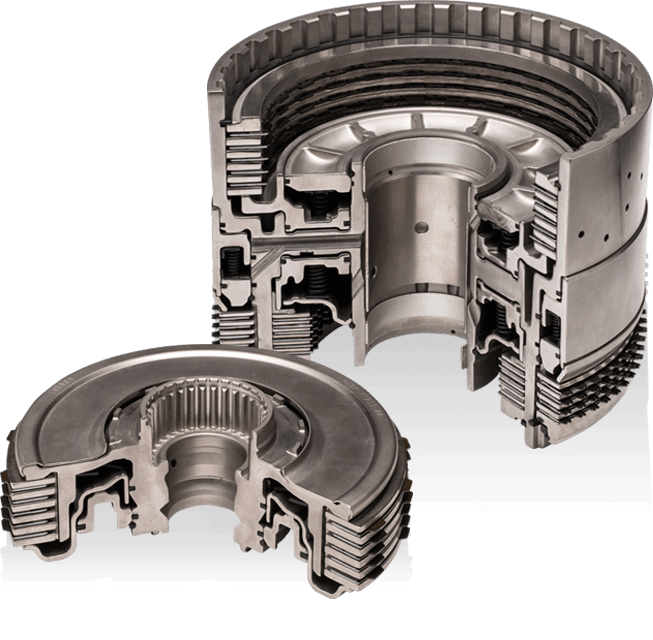
As one of the leading innovators of precision aluminum casting, FCC-NA has spent decades honing its expertise in quality control in aluminum castings for clutch manufacturing.
Learn More About How FCC-NA Is Leading Clutch Manufacturer With Aluminum Castings
Understanding Quality Control
Quality control represents the backbone of manufacturing excellence, especially when it comes to aluminum casting where precision and reliability are a must. It ensures that the products not only meet but exceed the expectations of customers and industry standards.
Definition and Significance
Quality control in manufacturing refers to the processes and measures implemented to monitor the quality of the materials and the products in the production cycle. In aluminum casting, this means ensuring that each casting is produced to the specified design, free from defects, and meets or exceeds the performance standards set by the industry and clients.
The importance of quality control cannot be overstated as it directly impacts the reliability, safety, and durability of the final products. It also plays a critical role in managing production costs, reducing waste, and maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction.
Role in Aluminum Casting Industry
Quality control in aluminum castings takes on an even greater importance due to the complex nature of casting processes and the diverse applications of aluminum products. The role of quality control here encompasses a complete range of activities, from the sampling inspection of raw materials and monitoring the casting process, to the final inspection of finished products.
It includes verifying the accuracy of molds, controlling the melting and pouring temperatures, and testing the mechanical properties of castings. Effective quality control practices, done by quality engineering in manufacturing, help in identifying and rectifying defects at early stages, ensuring the consistency of production, and facilitating continuous improvement in processes and products. This is essential not only for fulfilling stringent industry regulations but also for maintaining a competitive edge in the market by producing high-quality, reliable aluminum castings.
To learn more about how aluminum casting plays a crucial role in rapid prototyping and testing designs, explore our detailed guide on rapid prototyping in aluminum casting.
Standards and Regulations
To produce aluminum castings that meet the highest benchmarks of quality, adherence to international standards and regulatory compliance is paramount. These frameworks not only serve to guide manufacturers in achieving excellence but also ensure that products are safe, reliable, and consistent across the board.
International Standards for Aluminum Castings
International standards for aluminum castings provide a comprehensive set of guidelines and specifications designed to ensure the quality, performance, and safety of casting products. Organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) develop these standards, which are widely recognized and adopted across the globe.
For instance, ISO standards like ISO 9001 for a quality management system and ISO 14001 for environmental management systems are crucial for ensuring continuous improvement in aluminum casting operations. Similarly, ASTM B26/B26M covers the standard specification for aluminum alloys and sand castings, detailing the requirements for the chemical composition, mechanical properties, and quality of products. These standards not only assist manufacturers in meeting international quality benchmarks but also facilitate trade by harmonizing technical specifications on a global scale.
Regulatory Bodies and Compliance Requirements
Regulatory bodies play a critical role in overseeing the adherence to these standards and managing the compliance requirements for aluminum castings. In the United States, regulatory agencies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) set guidelines for safe manufacturing practices and environmental compliance, respectively.
Compliance with these regulations is not just a matter of legal requirement but also a testament to a company’s commitment to safety, sustainability, and quality. Manufacturers must be vigilant in keeping abreast of any changes in regulations, conducting regular audits, and ensuring that all aspects of their production processes, from raw material procurement to final product quality testing, comply with both domestic and international legal standards. This rigorous attention to compliance not only minimizes the risk of legal and financial penalties but also enhances a company’s reputation in the highly competitive aluminum casting market.
Quality Control Techniques
Diving deeper into the essence of maintaining quality control in aluminum casting, we encounter specific techniques that are pivotal to the industry’s success.
To further improve the reliability and precision of your aluminum castings, adopting advanced quality control techniques in forging can address common defects and ensure higher-quality outcomes.
Visual Inspection
Visual inspection is the most fundamental quality control technique used in aluminum casting. It involves a thorough examination of the casting’s surface by skilled inspectors to identify any visible defects such as cracks, porosity, or misruns. This method is pivotal in the early detection of surface imperfections that could compromise the integrity and performance of the casting. Visual inspection can be enhanced with the use of magnification tools and specialized lighting to detect finer defects that are not visible to the naked eye. Ensuring a casting passes visual inspection is a critical step before it proceeds to further testing and finishing processes.
Dimensional Inspection
Dimensional inspection entails the precise measurement and verification of the geometric dimensions of a casting to ensure they align with the specified design tolerances. This process can be conducted using various tools, from traditional calipers and micrometers to advanced technologies like Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) and laser scanning. Dimensional inspection guarantees that each casting adheres to the exact design specifications required for the component to function correctly in its final application. It is a critical step in quality control in aluminum castings that helps avoid costly errors and product rejections.
Once dimensional inspections ensure accuracy, further surface finishing techniques are applied to refine the casting for its final use. Learn more about these processes and how surface finishing in aluminum casting enhances both the durability and aesthetics of your products
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Methods
Non-Destructive Testing Methods are employed to assess the internal quality and surface integrity of castings without damaging them. These techniques provide critical information about the material properties, detect internal defects, and ensure the reliability of the casting under operational stresses.
Common NDT methods used in the aluminum casting industry include X-ray radiography, ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle testing, and dye penetrant inspection. Each method has its unique advantages and is chosen based on the type of casting and the nature of potential defects. By deploying NDT methods, manufacturers can certify the quality of their castings, thereby instilling confidence in their customers regarding the product’s durability and performance.
To further enhance quality control, precision aluminum die casting is vital in achieving superior manufacturing accuracy. Our high-precision manufacturing methods are critical in ensuring the production of lightweight and durable components. Learn more about how advanced aluminum casting technology supports high-quality, defect-free products.
Statistical Process Control (SPC) in Aluminum Casting
Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a methodological approach utilized to monitor and control a process by using statistical methods. Its primary goal is to ensure that the process operates efficiently, producing more specification-conforming products with less waste (rework or scrap).
SPC does this by monitoring and controlling the process through data visualization tools such as control charts, which help to identify and correct problems as they occur. By analyzing the data generated from the die-casting process, manufacturers can detect early signs of trouble and take preventative action before defects occur, leading to more consistent and higher-quality outcomes.
Application in Aluminum Casting Industry
In the aluminum casting industry, SPC is applied to various stages of the production process, from the melting and creation of aluminum alloy materials to the final casting and finishing stages. By monitoring key quality characteristics such as casting temperature, pressure, and cooling rates, SPC enables foundries to maintain tight control over their casting processes.
This detailed oversight helps in identifying variability and deviations from the set process parameters, which are critical for producing castings that meet strict specifications and quality standards. The implementation of SPC in aluminum casting not only improves the quality and reliability of the castings but also enhances operational efficiency by reducing waste, lowering costs, and increasing customer satisfaction. Through the effective use of SPC tools and techniques, aluminum casting manufacturers can achieve a competitive edge by continuously improving their processes and products.
Defects and Common Issues
In the process of aluminum casting, certain defects and common issues can adversely affect the quality and performance of the final product. Identifying and understanding these imperfections is crucial for manufacturers to enhance the reliability and integrity of their castings.
Porosity
Porosity is one of the most common defects encountered in aluminum castings, characterized by the presence of small holes or voids within the material. These voids can form due to trapped gas during the casting process or as shrinkage cavities when the material solidifies and cools.
Porosity undermines the mechanical strength and pressure tightness of the casting, making it less reliable for critical applications. Manufacturers aim to minimize porosity through careful control of the casting process, including optimizing the mold design, controlling the melt quality, and employing vacuum casting techniques.
Inclusions
Inclusions are foreign materials trapped within the casting that can significantly compromise its quality and strength. These impurities can include bits of slag, oxide films, sand from the mold, or other debris that gets incorporated into the aluminum during melting and pouring.
Inclusions act as stress concentrators and can initiate cracks under load, leading to premature failure of the casting. To reduce the risk of inclusions, foundries implement rigorous melting and filtration procedures to ensure the cleanliness of the metal before it is poured into the mold.
Surface Defects
Surface defects encompass a variety of imperfections found on the exterior of aluminum castings, such as scratches, scuffs, dents, and misruns. These flaws can occur due to issues with the mold, improper handling of the cast parts, or the turbulence of the molten aluminum during pouring.
While some surface defects may be aesthetic and not significantly impact the functional performance of the casting, others can lead to corrosion or weaken the part’s structural integrity. Effective preventative measures include the maintenance of molds, controlled pouring techniques and post-casting surface quality treatments.
Quality Control In Aluminum Castings: Final Thoughts
The meticulous implementation of Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) methods and Statistical Process Control (SPC) significantly enhances the quality, reliability, and efficiency of quality control in aluminum casting. By proactively identifying and mitigating defects such as porosity, inclusions, and surface imperfections, manufacturers are able to produce castings that meet the highest standards of performance and durability. The aluminum casting industry’s commitment to these practices not only serves to fulfill stringent quality specifications but also fosters trust and satisfaction among customers.
FCC-NA is at the forefront of aluminum casting excellence and innovation in clutch manufacturing. By continuously improving our processes and embracing technological advancements, we strive to remain a leader in the aluminum casting industry and provide unparalleled products and services to meet the evolving needs of our clients.
Learn More About How FCC-NA Is Leading Clutch Manufacturer With Aluminum Castings