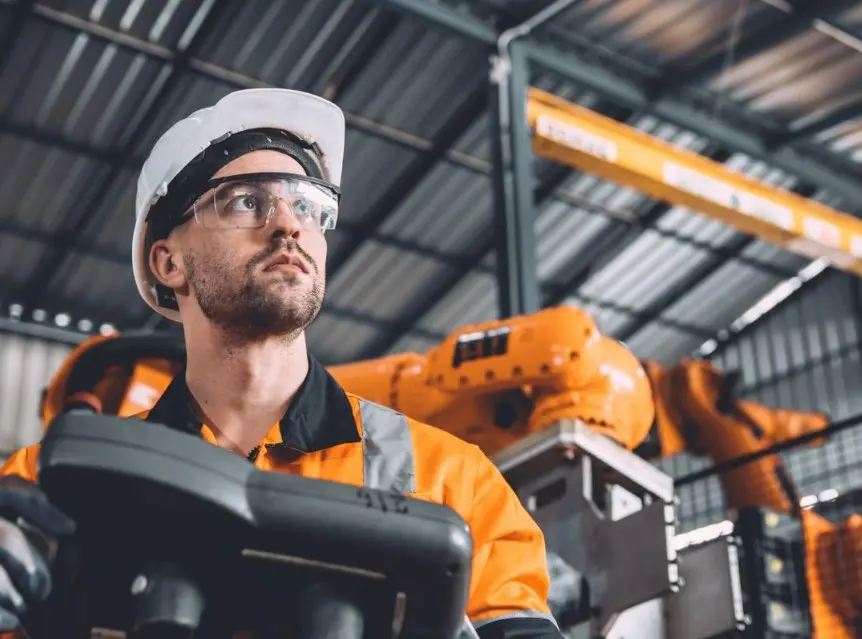
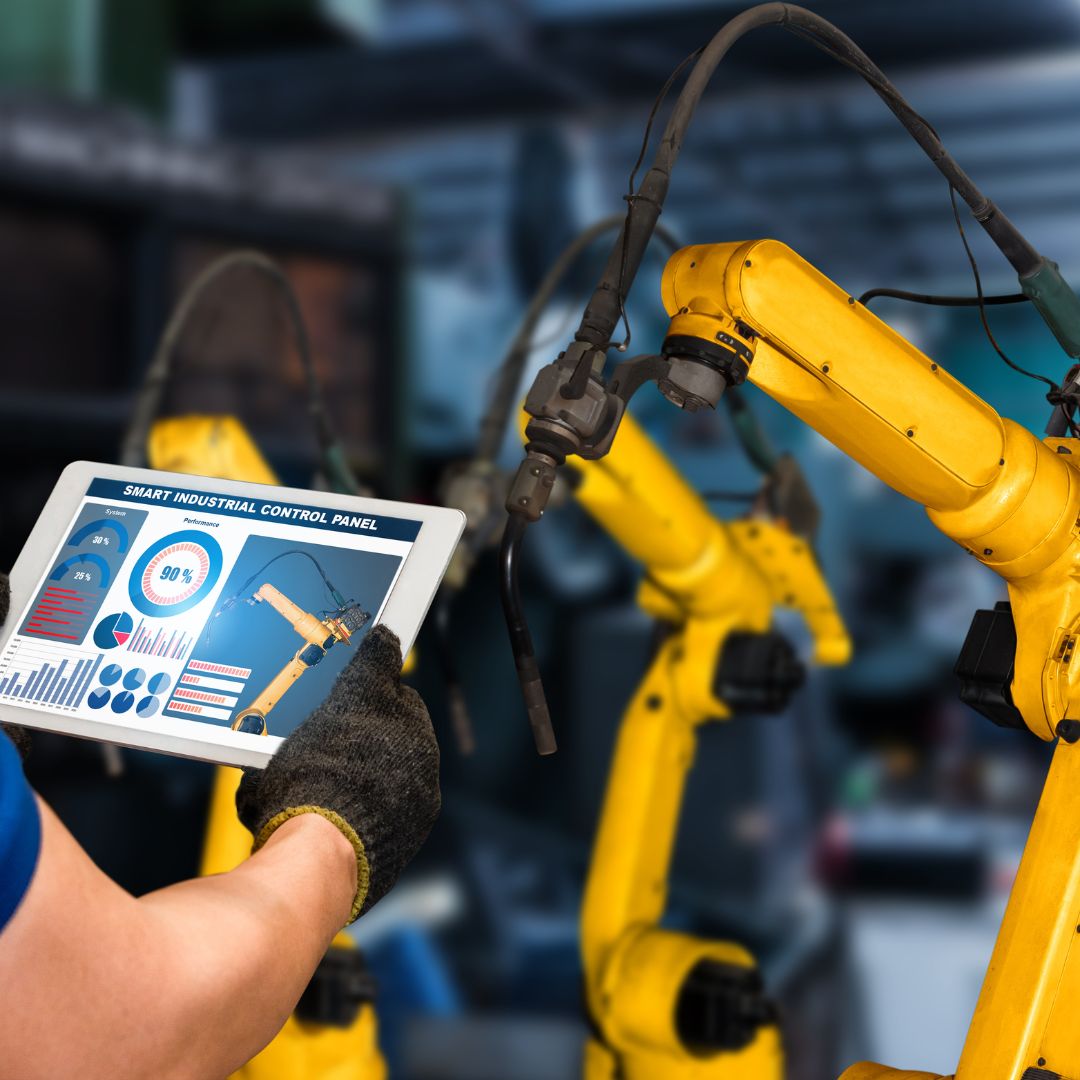
Robotics and automation are rapidly transforming industries across the globe, driving a new era of innovation and efficiency. So what are robotics and automation? Robotics is the design, construction, operation, and application of programmable machines known as robots. These robots are capable of autonomously sensing their surroundings and executing tasks either independently or with human collaboration.
Automation, on the other hand, entails the utilization of technology to regulate and manage machines or processes with minimal human involvement. Robotic process automation can range from basic systems like timers to sophisticated AI-driven robotic systems.
This article by FCC embarks on an exploration of these transformative technologies, delving into how both have revolutionized the industrial sector and the profound ramifications on contemporary society. Drawing from over 80 years of manufacturing and metalworking expertise, FCC has leveraged robotics and industrial automation to refine numerous techniques employed in our clutch-making process.
Learn More About Our Innovative Technology Today!
Historical Evolution
The history of robotics and automation dates back centuries, but significant advancements have occurred in the last few decades. In the mid-20th century, industrial robots were introduced in manufacturing, primarily for tasks like assembly and welding. These early robots were large, stationary machines programmed to perform specific tasks repeatedly.
As technology progressed, robots became more sophisticated, incorporating sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning algorithms. They evolved from being confined to factory floors to being utilized in diverse environments, including space exploration, medical surgeries, and household chores.
Automation has also evolved alongside robotics, with the development of computer numerical control (CNC) systems in the 1950s, leading to automated manufacturing processes. The integration of sensors, actuators, and control systems enabled machines to operate autonomously, optimizing production and reducing costs.
Importance in Modern Society
The role of robotics and automation in modern society cannot be overstated. They profoundly impact modern society, revolutionizing industries for enhanced efficiency and safety. Robotics and automation execute tasks swiftly and precisely, boosting productivity while minimizing errors. By automating hazardous duties, they improve workplace safety, reducing accidents.
Despite initial costs, they cut labor expenses and waste, optimizing resource allocation for long-term financial savings. Advanced automation systems ensure consistent product quality by streamlining operations with unwavering precision, yielding superior products.
Types of Robotics and Automation
There are different types of robotics and automation:
Industrial Robotics
Industrial robotics focuses on the design, development, and implementation of robotic systems for industrial applications.
Manufacturing
Industrial robots revolutionize manufacturing. They excel in tasks from welding to packaging in the automotive, electronics, and consumer goods industries. In automotive manufacturing, they ensure precision and efficiency in tasks like component assembly, spot welding, and vehicle painting.
Assembly Lines
Assembly line robots automate repetitive assembly tasks alongside human workers, handling tasks such as component placement, bolt fastening, and quality inspection. In automotive production, they ensure consistency and speed, contributing significantly to vehicle and individual parts assembly.
Robotics and industrial automation systems have allowed us here at FCC to explore the possibilities while constantly improving our very own joining technology. Robotics paved the way for Fcc to offer an extensive array of welding and joining technologies, spanning TIG Welding, MIG Welding, Plasma Welding, Electron Beam Welding, Laser Beam Welding, Spot Welding, Projection Welding, Ultrasonic Joining, and Ring Mash Joining.
Explore Our Welding & Joining Technologies Streamlined With Robotics!
Service Robotics
Service robotics focuses on designing, developing, and deploying robots to perform tasks and provide services in non-industrial environments, primarily to assist humans in various daily activities.
Healthcare
Healthcare robots aid medical professionals in patient care, surgery, rehabilitation, and telemedicine. They deliver medications, monitor patients, assist in surgery, provide prosthetics, and offer social engagement for mental health support.
Domestic Use
Domestic service robots simplify household chores, offering assistance with tasks like cleaning and providing companionship for the elderly or entertainment for children. They save time and effort by automating cleaning, maintenance, and security duties.
Military Robotics
Military robotics refers to the use of robotic systems and technologies for military applications. These robotic systems are designed to operate in hostile or dangerous environments where human presence may be impractical, risky, or impossible.
Surveillance
Military robots aid in reconnaissance and surveillance. They can be equipped with sensors and cameras for patrolling borders, monitoring conflict zones, and gathering intelligence. They enhance situational awareness, minimize risks for soldiers, and support informed decision-making in hazardous environments.
Combat
Autonomous combat robots, though in development and ethically sensitive, pose questions on warfare’s future. They may reduce human casualties but also raise concerns about accountability and unintended harm. Armed for offensive and defensive tasks, they have the potential to enhance military operations’ effectiveness and safety, performing duties like bomb disposal and perimeter security.
Advantages of Robotics and Automation
The integration of robotics and automation is reshaping industries and our daily lives, offering numerous advantages across various sectors. Take for instance the need for consistency and efficiency in the making of clutches in
Increased Efficiency
Increased efficiency is evident through robotics and automation, where robots consistently surpass humans in task completion, accelerating production rates and reducing lead times. By eliminating inefficiencies caused by human factors like fatigue and distractions, automation ensures seamless operations. Moreover, it frees human workers to focus on more intricate and creative tasks.
Cost Reduction
Robots and automation systems initially require significant investment but yield substantial long-term savings through reduced labor costs, increased efficiency, and lower error rates. In the end, however, enhanced production output and decreased waste contribute to cost-reduction efforts.
Improved Safety
Industrial automation significantly enhances safety by minimizing human exposure to hazardous tasks, chemicals, and heavy machinery. Robots handle repetitive and physically demanding tasks, reducing the risk of worker injuries. Artificial intelligence ensures precision and consistency, minimizing accidents and product defects.
Enhanced Accuracy
Robotics excel in accuracy, executing tasks with precise movements and exceptional repeatability, surpassing manual labor. This reduces errors and defects, elevating product quality and ensuring consistency, especially in precision-demanding fields like surgery or microchip assembly.
Scalability
Another hallmark of automation is scalability. Scalability in automation enables businesses to adjust to fluctuating demands effortlessly by swiftly deploying additional robots or software automation control systems. This agility facilitates rapid responses to market fluctuations, optimizing production alignment with prevailing needs. This may also be why 58% of US managers feel that robotics and intelligent process automation streamline repetitive tasks better than their human counterparts. Particularly beneficial in industries with seasonal demands or unpredictable production requirements, scalability enhances competitiveness and resilience in dynamic market environments.
Robotics and Automation in Various Industries
Robotics and automation have permeated nearly every industry. It has revolutionized workflows, boosted efficiency, and created exciting possibilities. Let’s explore how these technologies are impacting and shaping five key sectors.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, robotics and automation are essential. They streamline manufacturing tasks like welding, painting, and assembling components with precision. This results in enhanced production lines and maintained quality standards. Automated guided vehicles optimize warehouse material handling, and robotics with advanced vision systems ensure vehicle quality control. The future holds promise for autonomous vehicles, representing a significant frontier in automotive technology.
Take for instance the need for consistency and efficiency in the making of automotive clutches at FCC. Our core technology requires the innovation of robotics and automation technology to meet the standards that our clutches are known for. Across a spectrum spanning from 50cc to 2,300cc, whether on-road or off-road, the pinnacle of our motorcycle and ATV design efficiency is found in our standard clutch.
Learn More About Our Wet Multi-Plate Clutch Today!
Healthcare Sector
In the healthcare sector, robotics and automation have transformed patient care. Robotic arms assist in surgery, enhancing both precision and safety. Robotic exoskeletons aid rehabilitation, improving mobility post-surgery or injury. Automation streamlines pharmacy processes, and reduces errors in medication dispensing. Telemedicine has even utilized remote-controlled robots for virtual patient examinations, expanding healthcare access.
Agriculture
In agriculture, robotics and automation are reshaping traditional practices for efficiency and sustainability. With this in mind, the global agriculture robotics market is expected to grow by 18% CAGR by 2033. Autonomous tractors and drones optimize planting and harvesting, reducing reliance on manual labor and improving yields. Automated milking robots enhance animal welfare and production. Data-driven farming techniques empower informed decisions, maximizing yield and sustainability. Automated sorting and packaging systems streamline post-harvest processing, reducing food waste. These innovations transform agriculture, meeting modern challenges while ensuring environmental stewardship and economic viability.
Logistics and Supply Chain
Robotics and automation drive efficiency and precision in the logistics and supply chain sector, while reducing costs and delivery times. Warehouse robots have optimized workflow by picking, packing, and sorting goods swiftly and accurately. Then drones and autonomous trucks expedite deliveries. In the same breadth, automated inventory systems track stock in real time, minimizing stockouts. While sorting centers streamline parcel handling, enhancing capacity.
Construction
In the construction industry, robotics and automation are reshaping traditional practices, driving efficiency, safety, and quality across various facets of the building process. Robotic arms lay bricks swiftly and precisely, reducing time and labor costs. Remote-controlled robots handle hazardous tasks, enhancing worker safety. Automated factories produce prefabricated building components, speeding up construction and ensuring quality. Drones improve accuracy in surveying and inspections, contributing to project success. These innovations revolutionize construction, promoting safer, faster, and more efficient building practices.
Impact on Employment and Workforce
Despite the benefits of automation technology observed thus far, the rise of robotics and automation raises concerns about its impact on the workforce.
Job Creation vs. Job Displacement
Robotics and automation have the potential to both create and displace jobs, depending on how they are implemented and integrated into various industries. While they may replace manual tasks for example in the assembly line, they also generate employment in programming, maintenance, and data analysis. Industries adopting automation can undergo shifts in job roles, with some becoming obsolete and others emerging to meet automated system needs.
The truth is impact varies across sectors and regions, with some gaining productivity and competitiveness while others may see job losses.
Reskilling and Upskilling Initiatives
To address the challenges of job displacement and prepare the workforce for the future of work, reskilling and upskilling initiatives are essential. Programs offer training in digital skills and technical competencies essential for adapting to automation. Reskilling includes vocational training and online courses tailored to industry needs while upskilling enhances existing workers’ skills for new roles or advanced responsibilities, leveraging automation for productivity and innovation.
Future Work Trends
The rise of robotics and automation is reshaping the nature of work, leading to several emerging trends in the labor market:
- Growth of Gig Economy: Automation enables greater flexibility and remote work opportunities, leading to the growth of the gig economy and freelance workforce.
- Demand for Digital Skills: As automation becomes more prevalent, there is an increasing demand for workers with digital skills such as programming, data analysis, and AI expertise.
- Focus on Soft Skills: While technical skills are important, soft skills such as creativity, adaptability, and emotional intelligence become increasingly valuable in a highly automated workforce.
- Human-Machine Collaboration: The future of work will likely involve closer collaboration between humans and machines, with humans focusing on tasks that require empathy, creativity, and critical thinking, while machines handle repetitive and routine tasks.
- Lifelong Learning: Continuous learning and adaptation will be essential for workers to stay relevant in a rapidly changing labor market, with a shift towards lifelong learning and ongoing skill development.
Technological Innovations in Robotics
The field of robotics is experiencing a period of rapid evolution, fueled by cutting-edge advancements in various technological domains. Here, we explore some of the most exciting innovations shaping the future of robots:
Artificial Intelligence Integration
Artificial intelligence (AI) integration represents a pivotal advancement in robotics. It enables machines to perceive, decide, and learn. Combined with robots, AI unlocks cognitive capabilities for tackling complex tasks and adapting to dynamic environments. AI algorithms analyze sensor data for informed decision-making. Natural language processing (NLP) enables robots to comprehend and interact with human language, fostering seamless collaboration. This transformative shift in robotics enhances productivity, efficiency, and human-machine interaction across domains.
Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms enhance task handling, perception, and interaction. Reinforcement learning improves performance in uncertain tasks. Deep machine learning processes complex data for pattern recognition and task execution. Machine learning enables the customization of robot behavior for personalized experiences and collaboration. These advancements enhance adaptability, perception, and responsiveness, opening doors for innovative applications.
Sensor Technology Advancements
Sensor technology advancements propel robotics forward, as they enhance perception and safety. High-resolution cameras and 3D sensors enable precise object recognition and navigation. Tactile sensors on the other hand are capable of mimicking human touch, aiding delicate tasks like assembly. Multimodal sensor fusion integrates data from various sources for holistic environmental understanding. These innovations elevate robots’ capabilities and safety, driving advancements in robotics and automation.
Human-Robot Collaboration
Human-robot collaboration epitomizes a transformative paradigm in robotics, fostering synergistic partnerships between humans and machines across various domains. Collaborative robots or Cobots assist in assembly, improving productivity and safety. Telepresence robots extend capabilities into hazardous environments, minimizing human risk. Brain-computer interfaces enable intuitive control, enhancing collaboration. These advancements promise greater efficiency, advanced safety systems, and versatility through human expertise and robotic capabilities.
Environmental Sustainability in Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation, often associated with industrial landscapes and technological advancements, might seem counterintuitive to environmental sustainability. However, the sentiment is more nuanced. While potential downsides exist, these technologies also hold significant potential to contribute to a greener future.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency lies at the core of robotics and automation, driving significant reductions in energy consumption and promoting sustainability across various sectors. By minimizing errors and inefficiencies, robots conserve energy compared to human labor. Automation optimizes energy usage in factories and buildings, curbing unnecessary consumption. Robots maintain renewable energy infrastructure, enhancing efficiency in sectors like solar and wind power. These advancements promote a sustainable future.
Waste Reduction
Waste reduction is significantly advanced through the integration of robotics and automation, manifesting across various industries. Robotic process automation in manufacturing minimizes material wastage, reducing scrap and resource consumption. Robots efficiently sort and handle recyclables, enhancing recycling rates. Automated processes minimize chemical usage, promoting cleaner production and mitigating environmental impact. These applications underscore their pivotal role in fostering sustainable practices and environmental stewardship.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Sustainable manufacturing practices thrive with robotics and automation, driving efficiency and environmental stewardship across production processes. Closed-loop systems minimize waste by recycling materials between processes. Robotic systems prioritize sustainability, using recyclable materials and considering life cycle impacts. Automation enables remote monitoring, reducing travel emissions and enhancing efficiency. These integrated approaches ensure environmental responsibility and long-term viability in industrial operations.
Regulatory and Legal Frameworks
As robotics and automation rapidly transform our world, the need for robust regulatory and legal frameworks becomes increasingly necessary. These frameworks must address complex issues like safety, data privacy, and liability, ensuring responsible development and deployment of these technologies.
Safety Regulations
Ensuring safety in robotics requires a concerted effort to update existing frameworks to accommodate the evolving landscape of automation. While regulations such as occupational safety standards provide a foundation, existing frameworks need updates to address nuanced risks like robot autonomy and human-robot collaboration. International collaboration harmonizes safety standards, ensuring consistency globally. By fostering cooperation and adapting regulations, stakeholders prioritize safety in advancing robotics technology for both humans and machines.
Data Privacy Laws
The proliferation of robotics and automation introduces significant challenges regarding data privacy, necessitating a comprehensive approach to address emerging concerns. Robots collect extensive datasets, raising concerns about privacy infringement and misuse. Existing laws may not fully address these complexities. Safeguarding privacy requires transparency and user control over data usage and storage. Robust frameworks prioritizing transparency empower individuals to govern their data. By implementing such measures, stakeholders uphold and protect privacy rights amidst technological advancement.
Liability Issues
Navigating liability in robotics poses complex challenges, extending responsibility to manufacturers, developers, operators, and users. Clear legal frameworks are needed to allocate accountability and ensure compensation in accidents. As robots gain autonomy, ethical considerations arise regarding their moral agency and accountability for actions. Addressing liability requires balancing legal clarity with ethical guidance to foster fairness in robotic technology development and deployment.
Global Trends and Market Forecast
Robotics and automation are steadily shaping industries and societies worldwide, presenting a dynamic and evolving landscape.
Growth Projections
The robotics and automation industry is poised for substantial growth, with projections suggesting a market value of USD 283.19 billion by 2032, driven by a CAGR of 14.7% from 2023. Demand for efficiency and precision across sectors fuels this expansion. Advancements in AI, sensor tech, and human-robot collaboration further stimulate market growth. With industries increasingly embracing automation, the sector is primed for significant expansion, driven by innovation and the pursuit of operational excellence.
Regional Variances
Regional disparities in the robotics and automation sector underscore diverse market dynamics and adoption patterns across different continents. Asia Pacific leads with a 46% share, driven by automation adoption in manufacturing giants like China and Japan. North America emphasizes advanced and service robots, especially in medical and logistics. Europe focuses on industrial robotics and research in areas like humanoids. Emerging markets like Southeast Asia and Latin America show growing interest in automation, signaling potential for rapid adoption.
Key Players in the Industry
- Industrial Robot Manufacturers: Established players like ABB, Yaskawa, and Siemens remain dominant.
- Emerging Technology Companies: Companies like Boston Dynamics, Intuitive Surgical, and Berkshire Grey are pushing boundaries with advanced and service robots.
- Software and Infrastructure Providers: Companies like NVIDIA, Siemens PLM Software, and Rockwell Automation are crucial for robot software and control systems.
- Investment and Collaboration: Increased investments and collaborations between established players and new entrants are shaping the market landscape.
Summary of Key Points
The vast potential of robotics and automation lies in the capacity to drive economic growth, enhance resource utilization, and propel societal advancement. Yet, realizing these benefits necessitates a conscientious approach and proactive strategies to overcome obstacles.
It’s imperative to prioritize responsible development, fostering collaboration, and integrating ethical considerations. Through ongoing learning and concerted efforts, we can leverage robotics and automation to forge a sustainable and inclusive path toward a brighter future. As far as innovation is concerned, FCC will continue to leverage robot technology to automate tasks as part of our automation strategy.
The safety of our customers is our number one concern, therefore where possible we aim to automate and innovate to deliver advanced safety systems products of the highest quality.
Discover Why Our Automotive And Motorcycle Clutches Are Made For Your Future!